|
|
| 2008 |
|
P13-2008-1 (212.658)
Li Yong Chan, Pepyolyshev Yu.N.
The Change of Fast Reactivity Effects in the Operation of the IBR-2 Pulsed Reactor
The investigation of the dependence of main fast reactivity effects of the
IBR-2 pulsed reactor, i.e. isothermal effect, flow effect and effect of fast
power feedback, on the energy production has been carried out. It has been
shown that the main fluctuations of reactivity are correlated with the random
change of the temperature of sodium. The absolute isothermal coefficient of
reactivity weakly increases with the power production (by 20% during the
whole operation time of the reactor). The fast power reactivity coefficient
has decreased practically by a factor of 6 from -12bp/MW (in 1982, the start-up of the reactor)
to -2bp/MW (in 2006, the stop of operation) and has a
complicated dependence on the energy production. It has been shown that the
flow fluctuation of coolant sodium through the core is small and influences
weakly the random change of reactivity. The total sodium flow effect does
not practically change with the power production.
|
E10-2008-2 (279.088)
Soloviev A.G. et al.
Fitter. The Package for Fitting a Chosen Theoretical Multi-Parameter Function through a Set of Data Points.
Application to Experimental Data of the YuMO Spectrometer. Version 2.1.0. Long Write-Up and User's Guide
Fitter is a C++ program aimed to fit a chosen theoretical multi-parameter function through a set of data points.
The method of fitting is chi-square minimization. Moreover, the robust fitting method can be applied to Fitter.
Fitter was disigned to be used for a small-angle neutron scattering data analysis. Respective theoretical models are implemented in it.
Some common used models (Gaussian and polynomials) are also implemented for wider applicability.
|
E10-2008-3 (678.381)
Lebedev A.A., Ososkov G.A.
Track Reconstruction in the CBM TRD
A description, results and the current status of the track-finding routines
developed for the Transition Radiation Detector (TRD) of the CBM experiment
are presented. The track-finding algorithm is based on the Kalman Filter and
track following methods. Two different approaches have been used: a
stand-alone TRD track finder (using only TRD information) and an algorithm
based on the information from tracks found in preceding detectors.
Performances of the algorithms are presented. A detector layout study has
been performed in order to optimize the detector set-up while keeping high
reconstruction efficiency.
|
E18-2008-4 (339.243)
Steinnes E. et al.
Identification of Metal Emissions from Adjacent Point Sources in Northern
Norway Using Moss Biomonitoring and Factor Analysis
Atmospheric deposition of 34 trace metals around an iron-smelter complex in
a town in Northern Norway was studied in 2000 and 2005 using neutron
activation analysis of naturally growing moss. Specific contributions from
two adjacent but distinct smelters and changes in operation that had
occurred between the two sampling years were identified by factor analysis,
and relative contributions from the two sources at different sampling sites
were demonstrated by means of the factor scores. In 2000, emission from a
ferroalloy smelter (Smelter I) caused substantial deposition of Cr and Fe,
and this smelter was also the main source of Al, V, Co, Ni, As, Mo, and W.
Another nearby plant (Smelter II) recovering metals from used materials
caused considerable deposition of Mn and Zn and was also the main source of
Sb and W deposition. Following a transition from ferrochrome to
ferromanganese production, Smelter I in 2005 showed substantial deposition of
Mn. This smelter was also still the main source of Cr, Co, Ni, As, and Mo.
Smelter II maintained a considerable Zn deposition and showed increased
emissions of Sb and W. In most of the urban area the contribution from
Smelter~I~was dominant. An exception was two sites in the north-east
direction from the industries, where emissions from Smelter II dominated in
2000 as well as in 2005.
|
P6-2008-5 (192.664)
Filippov M.F. et al.
Investigation of U(VI) Sorption by Soil from the Region of Repository for Radioactive Waste
The uranium (VI) sorption onto soil from the region of repository for
radioactive waste was investigated. The experiments were carried out with
the 237U radioactive nuclide, which was produced in the photonuclear
reaction 237U(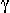 , n)237U at an electron accelerator, the
MT-25 microtron of the FLNR, JINR. The forms of the U(VI) state in the
solution for various uranium concentrations in the range pH 1-7 were
calculated using the programme "Speciation". , n)237U at an electron accelerator, the
MT-25 microtron of the FLNR, JINR. The forms of the U(VI) state in the
solution for various uranium concentrations in the range pH 1-7 were
calculated using the programme "Speciation".
|
2008-6 (1.080.378)
|
E1-2008-7 (4.317.785)
Artikov A., Bellettini G., Budagov J., Chlachidze G., Chokheli D., Glagolev V., Pukhov O.,
Sissakian A., Suslov I., Trovato M., Velev G.
Top-Quark Mass Measurement in the 2.1 fb-1 Tight Lepton
and Isolated Track Sample Using Neutrino f Weighting Method
We report on a measurement of the top quark mass in the
tight lepton and isolated track sample using the neutrino f weighting
method. After applying the selection cuts for the data sample with
the integrated luminosity of 2.1 fb-1 236 events were obtained. These events were reconstructed according
to the t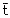 hypothesis and fitted as
a superposition of signal and combined background. For the expected
number of background 105.8 ± 12.9 wemeasure thetop quarkmass to
be Mtop = 167.7 ± 4.24.0 (stat.) ± 3.1(syst.) GeV/c2. hypothesis and fitted as
a superposition of signal and combined background. For the expected
number of background 105.8 ± 12.9 wemeasure thetop quarkmass to
be Mtop = 167.7 ± 4.24.0 (stat.) ± 3.1(syst.) GeV/c2.
|
P18-2008-8 (263.998)
Mosulishvili L.M. et al.
Development of Pharmaceutical Substances Based on Blue-Green Alga Spirulina рlatensis
A blue-green alga S. platensis biomass is used as a basis for the development of
pharmaceutical substances containing such vitally important trace elements
as selenium, chromium and iodine. Using neutron activation analysis the
possibility of target-oriented introduction of these elements into the S. platensis
biocomplexes retaining its protein composition and natural beneficial
properties has been proved. The curves of the dependence of the introduced
element accumulation in the Spirulina biomass on its concentration in a nutrient
medium, which make it possible to accurately measure out the required doses
of the specified element in a substance, have been obtained. The
peculiarities of interaction of various chromium forms (Cr(III) and Cr(VI))
with the S. platensis biomass have been studied. It has been found that from a nutrient
medium its cells mainly accumulate the vitally essential form of Cr(III) rather
than toxic Cr(VI). Using the EPR technique and colorimetry, it has been
demonstrated that the S. platensis substance enriched with Cr(III) is free from other
toxic chromium forms. The developed technique can be used in pharmaceutical
industry for the production of preparations containing Se, Cr, I, etc. on
the basis of S. platensis biomass with the preservation of its natural beneficial
properties and protein composition.
|
2008-9 (1.712.871)
|
2008-10 (1.255.991)
|
2008-11 (362.559)
|
E6-2008-12 (280.916)
Izosimov I.N., Kalinnikov V.G., Solnyshkin A.A.
Fine Structure of Strength Function for 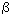 +/EC
Decay of 160gHo (25.6 min) +/EC
Decay of 160gHo (25.6 min)
A strength function for the 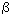 +/EC decay of the deformed
160gHo (25.6 min) nucleus has been obtained from the experimental data.
The fine structure of the strength function S +/EC decay of the deformed
160gHo (25.6 min) nucleus has been obtained from the experimental data.
The fine structure of the strength function S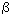 (E) is analyzed. It
is found to have a pronounced resonant structure for Gamow-Teller
transitions. In S (E) is analyzed. It
is found to have a pronounced resonant structure for Gamow-Teller
transitions. In S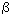 (E) with (E) with 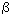  = +1 the
Gamow-Teller resonance is observed to split into two components. This
splitting is associated with anisotropy of isovector density oscillation in
deformed nuclei. The = +1 the
Gamow-Teller resonance is observed to split into two components. This
splitting is associated with anisotropy of isovector density oscillation in
deformed nuclei. The 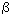 +/EC strength function for
first-forbidden transitions is obtained in the Coulomb ( +/EC strength function for
first-forbidden transitions is obtained in the Coulomb (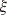 )
approximation. It is shown that S )
approximation. It is shown that S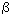 (E) for first-forbidden
transitions does not have a pronounced resonant structure. (E) for first-forbidden
transitions does not have a pronounced resonant structure.
|
2008-13 (1.040.343)
|
2008-14 (1.257.539)
|
2008-15 (1.005.574)
|
P9-2008-16 (459.844)
Kondratenko A.M., Kondratenko M.A., Filatov Yu.N.
The Spin Resonance Strength Calculation at the COSY Accelerator
Papers [1,2] study the effect of an rf-dipole on spin motion at the COSY accelerator (Jülich, Germany).
A difference between a theoretically calculated value of spin resonance strength for a deuteron beam and an experimentally
obtained value was found [2]. This paper shows that the difference between the experimental data and the theoretical
calculation of the strength of a spin resonance, induced by modulated radial magnetic fields, can be explained by using the spin response function.
|
2008-17 (793.272)
|
E5-2008-18 (108.871)
Shlyk V.A.
Recursive Operations for Generating Vertices of Integer Partition Polytopes
Following the polyhedral approach to integer partitions, we look at the set
of partitions of any integer as a polytope (convex bounded polyhedron). So,
all partitions of a given number are completely defined by the vertices of
this polytope as their convex combinations. In this work, we introduce two
combinatorial operations on partitions and show that with their help all
vertices of any integer partition polytope can be recursively generated from
a considerably smaller subset of its support vertices.
|
2008-19 (748.185)
|
P9-2008-21 (410.748)
Savchenko O.V.
A Variant of the Proton Accelerator with a Divided Magnet for the
Medico-Technical Complex of the LNP, JINR
A variant of the proton accelerator with a divided magnet for the Medico-Technical
Complex of LNP, JINR, is proposed and considered, which, in comparison with the
initial variant [1], allows one to exclude from the general layout of the accelerator
eight constant magnets for consistency of declined trajectories with trajectories of
proton beams in magnetic mirrors, reduce by half the number of the used magnetic
quadrupole lenses and therefore simplify the construction of the whole accelerator.
Besides, elimination of side defocusing in the vertical plane due to declined
trajectories in the new accelerator variant will result in a substantial rising
of the accelerator acceptance in the vertical plane and decreasing of the requirements
on precision of tune focusing of magnetic quadrupole lenses in that plane.
|
P9-2008-22 (659.606)
Savchenko O.V.
New Proposals for the External Injection into the JINR Phasotron and
Broadening of Its Application Possibilities
New methods of external injection into the JINR Phasotron are proposed and considered.
The basic feature of the third method consists in using the H--ions beam for
acceleration up to the energy 16 MeV in the U-115T isochronous cyclotron with a beam
intensity up to 500  A, developed and created at the Department of New Accelerators,
and the compact (about 1 m in diameter) storage ring for H--ions, designed for the
same energy and rigidity of the magnetic focusing, providing retention up to
4 A, developed and created at the Department of New Accelerators,
and the compact (about 1 m in diameter) storage ring for H--ions, designed for the
same energy and rigidity of the magnetic focusing, providing retention up to
4  1012 H--ions during 3.5 ms. In the fourth method the annular zone
inside the Phasotron chamber is proposed to be used as a storage ring.
Fast, one-turn extraction of the proton beam with an intensity increased
by an order of magnitude from the JINR Phasotron chamber on the basis of the
impulsive magnetic deflector and supplementary ferrous magnetic channel is considered.
Possible fields of application of the extracted proton beam with a duration
of the impulse of ~ 10 ns and frequency reccurrence 250 Hz are outlined,
in particular, creation at the JINR of a pulsed neutron source of
a superhigh resolution. 1012 H--ions during 3.5 ms. In the fourth method the annular zone
inside the Phasotron chamber is proposed to be used as a storage ring.
Fast, one-turn extraction of the proton beam with an intensity increased
by an order of magnitude from the JINR Phasotron chamber on the basis of the
impulsive magnetic deflector and supplementary ferrous magnetic channel is considered.
Possible fields of application of the extracted proton beam with a duration
of the impulse of ~ 10 ns and frequency reccurrence 250 Hz are outlined,
in particular, creation at the JINR of a pulsed neutron source of
a superhigh resolution.
|
P10-2008-23 (456.895)
Kirilov A.S. et al.
Organization of Remote Control of Spectrometers at the IBR-2M Reactor
The development of network infrastructure in Dubna creates conditions for the remote supervision/control of experiment at the IBR-2M
reactor beyond the JINR local network. The opportunity of observing an experiment from outside makes it possible to respond to errors or unforeseen
situations, to save the reactor time. The principles of organization and peculiarities of implementation of the WebSonix system consisting of the
central web-site and communication facilities for spectrometers are considered in the paper. The system allows one to reflect the actual condition
of all the components of the instrument, survey log files, visualize the accumulated spectra and to control the experimental procedure on the
instruments controlled by the software complex Sonix+ (OS Windows XP). The system is an independent instrument, it is easy to extend or change
and easy to adapt to the instrument data specifics. The system is implemented using the PHP and Python scripts. The OS GNU/Linux Debian and
web-server Apache 2 are installed on the web-site computer.
|
E18-2008-24 (301.328)
Meresova J. et al.
Еvaluation of Elemental Content in Airborne Particulate Matter in Low-Level Atmosphere of Bratislava
A one-year study on total airborne particulate matter has been undertaken in
the framework of air pollution project in Bratislava. Sixteen filter
samples were collected in 2004 in order to evaluate the level of pollution
and assess the potential environmental hazards in Bratislava. As a result of
two irradiations with neutrons and four gamma-spectrometric measurements the
concentrations of 30 chemical elements (Na , Al, Cl, K, Ca, Sc, Ti, V, Cr,
Mn, Fe, Ga, As, Se, Br, Rb, In, Sb, I, Cs, Ba, La, Sm, Dy, Tm, W, Au, Hg,
Th, U) were determined using instrumental neutron activation analysis
(INAA). Additionally, the concentrations of other 6 elements (Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn,
Cd, Pb) were measured by atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS). The
comparison with other European cities was carried out. Crustal enrichment
factors were calculated in order to distinguish the possible sources of
airborne particulate matter. For some elements elevated concentrations were
observed for the summer months. The other concentrations were relatively
stable over the year.
|
E6-2008-27 (319.811)
Zeynalov Sh., Zeynalova O., Smirnov V.
Application of Digital Signal-Processing Technique to Delayed-Neutron Yield Measurements on Thermal-Neutron Induced Fission of 237Np
The measurement procedure based on the continuous thermal-neutron
beam modulation with a mechanical chopper was developed for delayed-neutron yield
measurement of the thermal-neutron induced fission of 237Np. The idea
of the procedure is similar to that which is widely used in modern
communications for the nonauthorized data access prevention. The data is
modulated with predefined pattern before transmission to the public network
and only the recipient that has the modulation pattern is able to demodulate it upon reception. For the thermal-neutron induced reaction applications, the
thermal-neutron beam modulation pattern was used to demodulate the measured
delayed-neutron intensity signals on the detector output resulting in nonzero
output only for the detector signals correlated with the beam modulation
pattern. A comparison of the method with the conventional measurement
procedure was provided, and it was demonstrated that the cross-correlation
procedure has special features making it superior over the conventional one
when the measured value difference from the background is extremely small.
Due to strong sensitivity of measurement procedure on the modulation pattern
of the neutron beam, one can implement the modulation pattern of specific
shape to separate the effect of the thermal part of the beam from the higher
energy one in the most confident way in a particular experiment.
|
P1-2008-29 (445.858)
Vokal S. et al.
The Program of Polarization Studies and Methods to Accelerate the Polarized Beams of Protons and Light Nuclei at JINR Nuclotron
The program of polarization studies is represented. This program can considerably move our
knowledge how spin of hadrons and most light nuclei is constructed from spins of constituents. The polarized beams of light nuclei at Nuclotron are necessary for realization of
the program. The linear spin resonance strengths at Nuclotron which can lead to the effects of depolarization are calculated.
The application of the new method to preserve the beam polarization at spin resonance crossing at JINR Nuclotron is discussed.
|
P13-2008-30 (542.086)
Kalinin A.I. et al.
The Separator of the Mono-Energy Electrons
The separator of the mono-energy electrons employing two types of the
mini-orange form magnetic filters assemblies (by 6 magnets in each) is
described. The isotope 207Bi with radioactivity 240 kBq (7 mCi) is used as an
electron source radiating conversion electrons K1063 and K1770. Electrons
with the energy ~ 970 and ~ 1680 keV are accompanied by the 3- and
4-times radiation intensity increases depending on the assembly type
accordingly in comparison with measurements without magnetic filters, with
the energy resolution ~ 20 keV. The one-fold pumping-out of the cell
provided the instrument parameters constancy in the course of one month.
|
P11-2008-31 (396.708)
Melemov H.T., Boyadjiev T.L.
Numerical Solution of Systems ODE's on Embedded Intervals
In this paper a program for numerical solution of boundary value problems for ODE systems
given on the embedded intervals is described. Similar ODE's take place in physics of stacked Josephson
junctions with different lengths of the layers.
|
P4-2008-32 (865.826)
Sargsyan V.V. et al.
Quantum-Mechanical Description of Initial Stage of Fusion Reaction
Within the formalism of the reduced density matrix the process of capture of projectile
by a target at energies near the Coulomb barrier is considered. The influence of dissipation and fluctuations
is taken self-consistently into account. Using the calculated probabilities of the capture, averaged in all
mutual orientations of the deformed colliding nuclei, the evaporation residue cross-sections are calculated
for the asymmetric fusion reactions.
|
P18-2008-35 (554.957)
Kravets L.I. et al.
Preparation of Composite Membranes by Plasma Polymerization of Thiophene
The structure and electrotransport properties of poly(ethylene terephthalate) track membranes modified by thiophene plasma
have been investigated. We studied the influence of a degree of oxidation by iodine and UV-irradiation of a polymer layer obtained by plasma
on the membrane characteristics. It is shown that the deposition of the polymer on the surface of the track membrane by plasma polymerization
of thiophene in radio-frequency discharge in case of forming a semipermeable layer results in creation of composite membranes having in a
solution of electrolytes asymmetry of conductivity - a rectification effect. It is caused by presence in the membranes of two layers with
functional groups various in nature, and also by changing of the pore geometry. It is shown that doping of this polymer layer by iodine or
photo-oxidation causes increase in the density of a positive charge on its macromolecules, which results in changing the electrochemical
properties of the membranes treated by plasma. This allows one to obtain a wide spectrum of polymeric composite membranes with the
asymmetry of conductivity. Such type membranes can be used for creation of chemical and biochemical sensors.
|
E2-2008-36 (274.323)
Bunatian G.G.
The Ward-Takahashi Identities to Describe Nucleon and Pion Electroweak Transitions
For nucleons and pions, the relations among the propagators and
vertex functions to describe the vector electroweak transitions are
acquired as immediate corollary of symmetries of the hadron strong
and electroweak interactions. A point of value is that the
considered system comprises strongly interacting hadrons of
different sorts. The electromagnetic corrections to hadron vertex
functions and propagators are taken into account up to e2 order.
The sequels are discussed in the light of calculation of the
radiative corrections in describing the nucleon and pion
electroweak transitions.
|
P13-2008-38 (376.997)
Babkin V.A. et al.
Carbon Ion Beam for Radiotherapy at the JINR Nuclotron
The main results of several experiments in the framework of project
Med-Nuclotron are presented. The goal of the experiments is to measure the
main parameters of 12C ion beam and to draw the first conclusions about
the quality of the beam and possibility of using this beam for radiation
therapy.
The beam of carbon fully ionized ions with energy 500 MeV/u and intensity of
1 · 109 nucleus per spill was used. The principal property, which
makes heavy ions beam the most suitable radiation for tumor therapy - its
depth-dose distribution (Bragg peak). The shape measurements of the Bragg peak
with ionization chambers and diamond detector were performed.
|
E9-2008-39 (1.408.680)
Karamysheva G.A., Kostromin S.A.
Beam Dynamics Study in the C235 Cyclotron for Proton Therapy
Study of the beam dynamics in the C235 cyclotron dedicated to the proton therapy is presented.
Results of the computer simulations of the particle motion in the measured magnetic field are given.
Study of the resonance influence on the acceleration process was carried out.
The corresponding tolerances on the magnetic field imperfections and transverse beam parameters were defined using these simulations.
|
E1-2008-40 (257.295)
Beskrovnaia L.G. et al.
Verification of Monte-Carlo Transport Codes FLUKA, GEANT4 and SHIELD for
Radiation Protection Purposes at Relativistic Heavy-Ion Accelerators
The crucial problem for radiation shielding design at heavy-ion accelerator
facilities with beam energies to several GeV/n is the source term problem.
Experimental data on double differential neutron yields from thick target irradiated
with high-energy uranium nuclei are lacking. At present, there are not many
Monte-Carlo multipurpose codes that can work with primary high-energy uranium nuclei.
These codes use different physical models for simulation nucleus-nucleus reactions.
Therefore, verification of the codes with available experimental data is very important
for selection of the most reliable code for practical tasks. This paper presents
comparisons of the FLUKA, GEANT4 and SHIELD codes simulations with the experimental
data on neutron production at 1 GeV/n 238U beam interaction with thick Fe target.
|
E13-2008-41 (540.968)
Shabalin E., Fedorov A., Kulagin E., Kulikov S., Melikhov V., Shabalin D.
Experimental Study of Swelling of Irradiated Solid Methane During Annealing
Solid methane, notwithstanding its poor radiation properties,
is still widely in use at pulsed neutron sources. One of the specific problems
is radiolytic hydrogen gas pressure on the walls of a methane chamber during
annealing of methane. Results of experimental study of this phenomenon under
fast neutron irradiation with the help of a specially made low temperature
irradiation rig at the IBR-2 pulsed reactor are presented. Peak pressure
on the wall of the experimental capsule during heating of a sample irradiated
at 23-35 K appeared to have a maximum of 27 bar at the absorbed dose 20 MGy,
and then falls down with higher doses. Pressure always reached its peak
value at the temperature range of 72-79 K. Generally, three phases of
methane swelling during heating can be distinguished, each characterized
by proper rate and intensity.
|
P16-2008-42 (514.270)
Timoshenko G.N., Paraypan M., Florko B.V., Zaycev L.N.
Estimation of the Nuclotron Radiation Shielding Modernized for the NICA
Project
The results of the Nuclotron radiation shielding calculations at the
acceleration of uranium nuclei to energy 3.5 GeV/n and beam losses uniformly distributed
along the accelerator ring of 1·108 nuclei/s are
presented. The calculations were carried out by the FLUKA and GEANT4
codes for the simplified model of the accelerator placed within the
synchrophasotron tunnel in compliance with national standards on radiation
protection. The neutrons escaped from the Nuclotron shielding and
multiscattered in air and ground will form the radiation situation around
the modernized Nuclotron. The variant of the Nuclotron shielding design with the
use of synchrophasotron magnet element is proposed.
|
E11-2008-43 (270.426)
Sitnik I.M.
Modification of the FUMILI Minimization Package.
In memory of Prof. I.N.Silin
FUMILI renovation is suggested which allows the
following: a more convenient and friendly user interface; no restriction on
the number of parameters and experimental points; speed advantage
when the number of parameters is high enough; a possibility to define
analytically an arbitrary number of parameter derivatives.
An additional package of subroutines, including track reconstruction in the straw tube
chambers, is suggested. All programmes are written using FORTRAN-90.
|
P13-2008-44 (1.333.235)
Yudin I.P. et al.
Measurement of the Magnet Field Map for the Analysing Magnet of the "Delta-Sigma" Spectrometer
One of the main goals of the "Delta-Sigma-experiment" project is measurement of the energy behaviour of spin-dependent NN
observables A00kk(np), A00nn(np) and Rdp in the GeV region of the neutron beam. These observables are
determined by measurement of proton yields from the np  pn charge-exchange reaction at 0° using
a magnetic spectrometer. Measurements of the magnetic field map of the spectrometer magnet providing high accuracy in determining the proton momentum
were carried out. pn charge-exchange reaction at 0° using
a magnetic spectrometer. Measurements of the magnetic field map of the spectrometer magnet providing high accuracy in determining the proton momentum
were carried out.
The "Delta-Sigma" set-up is placed at building 205 of the LHE, JINR. The spectrometer magnet 2-SP-94-1V has the external sizes 2,95 x 2,12 x 1,62 m
and aperture 0,30 x 0,09 m. A three-component Hall probe was used. The measurement volume is 0,33 x 0,0645 x 1,02 m.
A description of the measuring equipment, method and results is presented. The results are used for analysis of the physical data.
|
E5-2008-45 (288.252)
Zhidkov P.E.
On the Eigenfunction Expansions Associated with Semilinear Sturm-Liouville-Type Problems
We consider semilinear second-order ordinary differential equations, mainly autonomous in the form
-u''=f(u)+lu, supplied with different sets of
standard boundary conditions. Here l is a real constant or it
plays the role of a spectral parameter. Mainly, we study problems in the interval (0,1).
It is shown that in this case each problem we deal with has an infinite sequence of solutions or eigenfunctions.
Our aim is to review recent results on basis properties of sequences of these solutions or eigenfunctions.
In a number of cases, it is proved that such a system is a basis in L2 (in addition, a Riesz or Bari basis).
In addition, we briefly consider a problem in the half-line (0, ). In this case,
the spectrum of the problem fills a half-line and an analog of the expansions into the Fourier integral occurs.
The proofs are mainly based on the Bari theorem and, in addition, on our general result on sufficient conditions
for a sequence of functions to be a Riesz basis in L2. ). In this case,
the spectrum of the problem fills a half-line and an analog of the expansions into the Fourier integral occurs.
The proofs are mainly based on the Bari theorem and, in addition, on our general result on sufficient conditions
for a sequence of functions to be a Riesz basis in L2.
|
P16-2008-46 (766.442)
Aleynikov V.E., Beskrovnaia L.G., Mokrov Y.V.
The Research for the Neutron Ambient Dose Possibility of Measurement
Using the Instrument Based on the 10B-Counter with
Moderator in the Fields at JINR Nuclear-Physics Installation
The results of the research for the neutron ambient dose equivalent H*(10)
possibility of measurement using the instrument based on the 10B-counter (СНМ-14) with polyethylene moderator in the fields of JINR
nuclear-physics installation have been presented. It was shown that
the instrument can be used to measure H*(10) of neutrons in the
energy range from 0.4 eV to 20 MeV with the uncertainty within 46% in
radiation monitoring at JINR. The use of the correction factors can extend
the energy range of the measurement of the neutron dose H*(10) up to
hundreds of MeV. Neutron spectra, which were measured in the fields of
nuclear installation of JINR earlier, places and conditions of
their measurement, are presented too.
|
P4-2008-48 (162.225)
Ignatovich V.K.
On Neutron Surface Waves
Recently the question of existence of neutron surface waves was discussed [1, 2].
In the given paper it is shown that such waves do not exist. The analysis of neutron wave
mechanics, electromagnetic and acoustical wave physics reveals why in the last two cases
the surface waves are not forbidden.
|
E3-2008-49 (177.655)
Ignatovich V.K.
Analytical Calculation of the Neutrons Spectrum
for Direct Measurement of n-n Scattering at the YAGUAR Pulsed Reactor
Analytical calculation of a single neutron detector
counts per YAGUAR reactor pulse is presented and comparison with coincidence scheme is given.
|
P18-2008-50 (942.580)
Nikitin A.N., Ivankina T.I., Ignatovich V.K.
Pecularities of P- and S-Wave Propagation through Textured Rocks
Using the data on quasi-compressional (Vp) and quasi-shear (Vs) wave velocities
measured on rock samples at high pressures and high temperatures, and
3D-velocities calculations based on orientation distribution functions of
rock-forming minerals obtained by neutron diffraction analysis, the typical
discrepancies between experimental and model parameters are revealed. The
theoretical analysis of P- and S-wave propagation through anisotropic media
is carried out. The study demonstrates that for an anisotropic inhomogeneous
media the experimental P- and S-wave velocities could not
coincide with numerical velocity calculations due to the physical correlation between
two types of waves - compressional and shear waves.
|
P11-2008-51 (416.252)
Bespalko E.V., Mikheev C.A., Puzynin I.V., Reznikov A.M., Tsvetkov V.P.
Bifurcations in One Astrophysical Model of Rotating Magnetized Politropics with a Small Index
A solution of the equation of hydrostatical equilibrium was obtained for rapidly
rotating gravitating magnetized polytropic with a small index n in linear approach by n.
An existence of bifurcation points of this configuration in the interval
0  n n  0.1161 was proved, in which solutions asymmetric about the axis of
rotation branch off. The analytic dependence of a parameter of asymmetry X on parameter values
of velocity of rotation e, index n, values of magnetic tension 0.1161 was proved, in which solutions asymmetric about the axis of
rotation branch off. The analytic dependence of a parameter of asymmetry X on parameter values
of velocity of rotation e, index n, values of magnetic tension 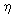 m was found.
The problem of shift of bifurcation points induced by magnetic tension was considered. The dependence
of acceleration of gravity at equator of configuration geq on parameters e and n
was investigated. For the first time it was proved that a series of rotating polytropes having bifurcation
points breaks at nk=0.1161, much earlier than the values specified in [6, 7]: nk=0.83 and
nk=0.808. It was shown that this effect was due to the essentially nonlinear dependence of
geq on n and connected with the rapidly growing equatorial radius req
according to the increase of the polytropic index n. m was found.
The problem of shift of bifurcation points induced by magnetic tension was considered. The dependence
of acceleration of gravity at equator of configuration geq on parameters e and n
was investigated. For the first time it was proved that a series of rotating polytropes having bifurcation
points breaks at nk=0.1161, much earlier than the values specified in [6, 7]: nk=0.83 and
nk=0.808. It was shown that this effect was due to the essentially nonlinear dependence of
geq on n and connected with the rapidly growing equatorial radius req
according to the increase of the polytropic index n.
|
P9-2008-53 (276.678)
Karamysheva G.A., Karamyshev O.V., Lepkina O.E.
Cyclotron Beam Dynamic Simulations in MATLAB
MATLAB is useful for beam dynamic simulations in cyclotrons.
Programming in an easy-to-use environment permits creation of models in a
short space of time. Advanced graphical tools of MATLAB give good
visualization features to created models. The beam dynamic modeling
results with an example of two different cyclotron designs are presented.
Programming with MATLAB opens wide possibilities of the development of
the complex program, able to perform complete block of calculations
required for the design of the accelerators.
|
E1-2008-54 (1.530.356)
Hashemi-Nezhad S.R., Zhuk I.V., Kievets M.,
Krivopustov M.I., Sosnin A.N., Westmeier W., Brandt R.
(On behalf of "Energy plus Transmutation" Collaboration)
Investigation of Spatial Distribution
of Fission-Rate of Natural Uranium Nuclei in the Blanket of Electronuclear Setup
"Energy plus Transmutation" at Dubna Nuclotron Proton Beam at Energy 1.5 GeV
The "Energy plus Transmutation" experimental setup of the Veksler and
Baldin Laboratory of High Energy Physics within the Joint Institute for Nuclear
Research (JINR) in Dubna, Russia, is a lead target (with a diameter of 8.4 cm and length of 45.6 cm) surrounded by a uranium blanket (weight 206.4 kg of
natural uranium). A polyethylene plus cadmium shield is placed around the
target-blanket assembly to modify the spallation and fission neutron spectra
in the system. The setup was irradiated by a proton beam of energy 1.5 GeV
using the Nuclotron accelerator.
In this work the spatial distribution of natural uranium fission-rate in the
assembly and fission-rate in the blanket was determined experimentally and
compared with Monte-Carlo predictions using the MCNPX 2.6C code. Besides
neutron-induced fission the calculations include the NatU(p, f),
NatU(p, f) as well as NatU(g, f) reactions. Good agreement between the
experimental and calculation results was obtained. The possible sources of
errors in the experiment and calculations are discussed in detail.
|
E2-2008-55 (156.502)
Fadeev N.G.
Inertial Frame Transformation Based on Lobachevsky Function and Some
Optical Phenomena (Michelson-Morley Experiment and Doppler Effect)
The inertial frame transformation based on the Lobachevsky function and some
of its properties are reminded. The results of introducing them into a physical
consideration of the Michelson experiment and standard Doppler effect in optics,
are presented. It is shown that the new transformation approves the negative result
obtained in the Michelson experiment in the same way as the Lorentz one. But the
crucial result is expected for the measurements performed with unequal lengths
of the interferometer optical arms and it will be in favour of the new one. In contrast
to Lorentz contraction the relativity requirements of the new transformation again lead
to two different formulas for the Doppler effect in optics as in acoustics.
|
E17-2008-56 (408.261)
Moskalenko V.A. et al.
Diagrammatic Theory for Anderson Impurity Model
A diagrammatic theory around atomic limit is proposed for the normal and superconducting
states of the Anderson impurity model. The impurity electrons have strong Coulomb
repulsion between them. This interaction is the main parameter of the theory. The
new method is based on the ordinary Wick theorem for conduction electrons and
generalized Wick theorem for strongly correlated impurity electrons.
For the mean value of evolution operator the linked cluster theorem
is proved and the Dyson-type equations for one-particle propagators of conduction
and impurity electrons in the normal and superconducting states of the system have
been established.
The behavior of the impurity electron spectral function has been studied.
The structure of the resonances and their properties are analyzed.
We have proved that the thermodynamic potential of this strongly
correlated system can be presented, after introduction of special integration by
the constant of hybridization strength, as the functional of the full Green function
of conduction electrons and its mass operator. The stationary property of this
potential related to the changes of the mass operator has been demonstrated as well.
|
E13-2008-58 (1.451.650)
Budagov J., Sabirov B., Sissakian A., Shirkov G., Sukhanova A., Basti A., Bedeshi F., Frasconi F., Linari S.
Stress Analysis of the Ti-SS Transition Joint
The bimetallic (titanium-stainless steel) transition sample in the ILC
cryomodule design was found to be leak-proof in the tests. Before manufacture and tests of
a larger-size sample, displacements and stresses in the transition element arising from its
being cooled from room temperature down to the liquid helium temperature were evaluated, and
the parameters for both versions (tubes of different diameters) were compared.
|
P11-2008-59 (191.146)
Zhanlav T., Mijiddorj R., Chuluunbaatar O.
The Continuous Analog of Newton's Method for Solving Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors of the Matrices
The continuous analog of Newton's method for solving eigenvalues of the matrices is proved.
Convergence of the iteration processes with an optimal iteration parameter is proved. The algorithm considered is applied also to a
nonlinear eigenvalue problem.
|
E11-2008-60 (146.674)
Zhanlav T., Mijiddorj R.
Integro Cubic Splines and Their Approximation Properties
It is shown that the difficulties in constructing the integro
cubic spline proposed by H.Behforooz [1] may be overcome using its
B-representation. The approximation properties of such a spline
are also considered.
|
E1-2008-61 (647.007)
Sharov V.I.
The Ratio Rdp of the Quasi-Elastic nd p(nn)
to the Elastic np p(nn)
to the Elastic np pn Charge-Exchange Process Yields
at 0o over 0.55-2.0 GeV Neutron Beam Energy Region:
1. Experimental Results pn Charge-Exchange Process Yields
at 0o over 0.55-2.0 GeV Neutron Beam Energy Region:
1. Experimental Results
New experimental results on ratio Rdp of the
quasi-elastic charge-exchange yield at 0oLab
for the nd p+(nn) reaction to the elastic
np p+(nn) reaction to the elastic
np pn charge-exchange yield are presented.
The measurements were carried out at the Nuclotron of JINR VBLHE
at neutron beam kinetic
energies of 0.55, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0 GeV.
The data were accumulated by means of the "Delta-Sigma"
set-up magnetic spectrometer with two sets of multiwire
proportional chambers located upstream and downstream of
the analyzing magnet. Inelastic processes were considerably
reduced by means of the additional detectors surrounding the hydrogen
and deuterium targets. The time-of-flight system was
applied to identify a detected particle.
The accumulated data treatment and analysis of possible
systematic errors are discussed.
The obtained Rdp values remain nearly constant with the
energy. The new data are compared with the existing
ones, which were measured up to 1 GeV.
The comparison of these data with the calculations of
Rdp obtained by using the invariant amplitude sets
from the GW/VPI phase-shift analysis was made in a
separate paper. pn charge-exchange yield are presented.
The measurements were carried out at the Nuclotron of JINR VBLHE
at neutron beam kinetic
energies of 0.55, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.0 GeV.
The data were accumulated by means of the "Delta-Sigma"
set-up magnetic spectrometer with two sets of multiwire
proportional chambers located upstream and downstream of
the analyzing magnet. Inelastic processes were considerably
reduced by means of the additional detectors surrounding the hydrogen
and deuterium targets. The time-of-flight system was
applied to identify a detected particle.
The accumulated data treatment and analysis of possible
systematic errors are discussed.
The obtained Rdp values remain nearly constant with the
energy. The new data are compared with the existing
ones, which were measured up to 1 GeV.
The comparison of these data with the calculations of
Rdp obtained by using the invariant amplitude sets
from the GW/VPI phase-shift analysis was made in a
separate paper.
|
E2-2008-62 (175.093)
Sharov V.I., Morozov A.A., Shindin R.A., Chernykh E.V., Nomofilov A.A., Strunov L.N.
The Ratio Rdp of the Quasi-Elastic nd  p(nn) to the Elastic
np p(nn) to the Elastic
np  pn Charge-Exchange Process Yields at 0° over 0.55-2.0 GeV Neutron Beam Energy Region: 2. Comparison of the Results with the Model Dependent Calculations pn Charge-Exchange Process Yields at 0° over 0.55-2.0 GeV Neutron Beam Energy Region: 2. Comparison of the Results with the Model Dependent Calculations
In our previous paper, the new experimental results on ratio Rdp
of the quasi-elastic charge-exchange yield at 0°Lab for the nd  p+(nn)
reaction to the elastic np p+(nn)
reaction to the elastic np  pn charge-exchange yield, were presented. The measurements
were carried out at the Nuclotron of the Veksler and Baldin Laboratory of High Energies of the Joint
Institute for Nuclear Research at the neutron beam kinetic energies of 0.55, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.8
and 2.0 GeV. In this paper, the comparison of these Rdp data with the Rdp calculations obtained
within the impulse approximation by using the invariant amplitude sets from the GW/VPI phase-shift analysis,
is made. The calculated Rdp values with the set of invariant amplitude data for the elastic
np pn charge-exchange yield, were presented. The measurements
were carried out at the Nuclotron of the Veksler and Baldin Laboratory of High Energies of the Joint
Institute for Nuclear Research at the neutron beam kinetic energies of 0.55, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.8
and 2.0 GeV. In this paper, the comparison of these Rdp data with the Rdp calculations obtained
within the impulse approximation by using the invariant amplitude sets from the GW/VPI phase-shift analysis,
is made. The calculated Rdp values with the set of invariant amplitude data for the elastic
np  pn charge exchange at pn charge exchange at  p,CM = 0° are in a good agreement with
the experimental data. It has been confirmed that at p,CM = 0° are in a good agreement with
the experimental data. It has been confirmed that at  p,CM = 0° the nd p,CM = 0° the nd  pnn
process is caused by the elastic np pnn
process is caused by the elastic np  pn charge-exchange reaction. Thus, it has been
shown that the obtained experimental Rdp results can be used for the Delta-Sigma experimental programme
to reduce the total ambiguity in the extraction of the amplitude real parts. pn charge-exchange reaction. Thus, it has been
shown that the obtained experimental Rdp results can be used for the Delta-Sigma experimental programme
to reduce the total ambiguity in the extraction of the amplitude real parts.
|
P4-2008-63 (715.139)
Ignatovich V.K., Radu F.
Reflection of Neutrons from Magnetic Systems with Fan-Like Magnetization
Analytical solution for neutron reflection and transmission of magnetic
mirrors with fan-like magnetization is found. The dependence of reflection
and transmission curves on neutron speed is shown. Resonant properties of
fan-like systems are analysed.
|
P13-2008-66 (490.254)
Ion M., Kozlov Z.A., Mateescu G., Padureanu I., Semenov V.A., Kraciun L., Rapeanu S.,
Morozov V.M., Oprea A.I., Oprea C., Puchkov A.V.
High-Temperature Thermostat TS-3000K for Neutron Investigations at the DIN-2PI Srectrometer at the IBR-2 Reactor
In FLNP JINR at the IBR-2 reactor a high-temperature thermostat TS-3000К
was put into operation which along with the DIN-2PI spectrometer is intended for investigation
of material atom dynamics at temperatures up to 3000 К. In paper the basic characteristics of the
thermostat and the results of the first neutron measurements are discussed.
|
P3-2008-67 (195.496)
Shabalin E.P.
On Nonregularity of Movement of a Spherical Bead Conveying Pneumatically in a Pipe
Kinematics of a solid spherical bead driven with gas flow along a cylindrical tube is considered.
The simplest theoretical analysis of how thresholds and ledges, formed by roughness of pipe walls, affect speed of a bead, is derived.
Inevitability of nonregularity of bead movement, that is, alternation of accelerations and decelerations, is concluded. Formulas for
estimation of both maximal and minimal speed of a bead at the given spatial distribution of thresholds and their height is derived.
Some theoretical assertions are proved experimentally. The investigation has been performed in the frame of a project of the pelletized
cold neutron moderator for the IBR-2M reactor.
|
P11-2008-68 (156.828)
Dolbilov A.G., Ivanov Yu.P.
Grid-System Element of LCG-2 in DLNP
We present here the description of the computer cluster at the
Dzhelepov Laboratory of Nuclear Problems of JINR, where the second Grid node
at JINR was realized. The configuration of the system, which allows effective
joint usage of cluster resources both for local users and for others within
the framework of the ATLAS collaboration is examined. Examples are given for
basic stages of preparing and running ordinary cluster jobs and with the
Grid usages, starting from obtaining CA certificates, submitting jobs and
retrieving the results. Perspectives of the cluster upgrade are discussed.
|
P13-2008-69 (612.907)
Abov Yu.G., Alfimenkov V.P., Lason L., Mareev Yu.D.,
Pikelner L.B., Tsulaya V.M., Tsulaya M.I., Salamatin I.M.
"Kolkhida" Instrument for Experimental Investigations of Interactions of Polarized Neutrons with Polarized Nuclei
In JINR at the IBR-2 pulsed reactor [1] the "Kolkhida"
setup intended for studies of neutron-optics phenomena in interactions of polarized
neutrons with polarized nuclei has been constructed. In particular, studies of nuclear
precession of neutron spin in a wide energy range from thermal to neutron resonance
energies are planned. The setup also makes it possible to investigate magnetic
properties using polarized neutrons.
In the given paper we present the description of the setup, its key parameters, as well as the
result of computer simulation of the experiment on neutron paramagnetic resonance shift.
|
E6-2008-71 (286.712)
Karamian S.A., Ur C.A., Adam J., Kalinnikov V.G., Lebedev N.A., Vostokin G.K., Collins C.B., Popescu I.I.
Spallation and Fission Products in the (p+179Hf) and
(p+natHf) Reactions
Production of the high-spin isomers of Hf and Lu has been experimentally
studied in the spallation reaction with intermediate energy protons. The
targets prepared of enriched 179Hf (91 %) and natHf have been
exposed to protons with energy range from 90 to 650 MeV using the
internal beams of the Dubna Phasotron accelerator. Activation yields of the
reaction products are measured by methods of g-spectroscopy and
radiochemistry. The production cross sections for 179m2Hf, 178m2Hf
and 177mLu have been found comparable to the values measured earlier
through spallation of Ta to Re targets. Thus, the exclusive reactions with
emission of only a few nucleons, like (p, p'), (p, p' n) and (p, 2pn), can transfer enough angular momentum to the product and provide
reasonable cross sections.
|
P2-2008-73 (249.295)
Kosmachev O.S.
The Problem of Quantum Numbers of the Lepton Sector
A unique approach to wave equations for stable and nonstable leptons has been
developed. The algorithm is based on four initial principles which are
necessary and sufficient conditions for obtaining the wave equations. The main
advantage and virtue of the proposed method is a possibility to describe and
enumerate all possible types of free equations for stable and unstable leptons
in the framework of a homogeneous Lorentz group by means of a unique approach
without using the Lagrange formalism.
|
P13-2008-74 (181.666)
Gurov Yu.B., Karpukhin V.S., Rozov S.V., Sandukovsky V.G., Borowicz D.,
Kwiatkowska J., Rajhel B., Jurkowski J.
Passivation of HPGe Detectors
The results of research of the oxide protective covering for
p-n junction of HPGe detectors are presented. In particular this covering
makes it possible to use detectors in the environment of liquid nitrogen without
capsulation. The simple technological method of formation of protective layer due to
processing detectors in the methanol is described. This protective layer reliably
protects p-n junction of detectors from influence of an environment. The characteristics
of protective oxide film are investigated by means of Raman effect of dispersion of light.
|
P13-2008-75 (661.560)
Aleev A.N.
Neutral Particle 5N Channel of the U-70 Accelerator (IHEP)
The 5N neutral particles channel at the U-70 accelerator (IHEP),
designed for producing a beam of neutrons of high intensity and greatest
possible energy, is described. The average energy of neutrons is
~ 51 GeV, intensity - up to 107 neutrons per spill.
This beam was used for investigation of charmed particles and narrow
baryon resonances in neutron-nucleus interactions and also for search
of exotic multi-quark states with the EXCHARM spectrometer.
|
P9-2008-76 (651.651)
Dolya S. N., Reshetnikova K. A.
Two Variants of Injection of Heavy Ions into the Nuclotron Booster
The acceleration of uranium ions with the charge Z = 32 and atomic mass
A = 238 is discussed.
In the first section of the spiral waveguide working at the frequency
f1 = 10 MHz with the RF power P = 3 MW, ions are accelerated from
Wi = 11.25 keV/nucleon to W1i = 500 keV/nucleon on the length
L1 = 2.5 m. The magnetic field focusing ions B1 = 1.5 T. The
second section working at the frequency f2 = 150 MHz has the length
L2 = 12.5 m. The focusing magnetic field B2 = 2 T. The final energy
of ions Wi2 = 5.6 MeV/nucleon.
The acceleration of ions in coaxial resonators begins from the energy
Wi = 84 keV/nucleon to Wi1 = 500 keV/nucleon on the length L1= 3.6 m
after crossing
30 resonators. The RF power of each resonator P = 50 kW, frequency
f2 = 150 MHz, high voltage on each gap E1 = 100 kV/cm. Focusing of
the ion beam is realized by quadrupole magnetic lenses between the
resonators. The gradient of the magnetic field G = 4.8 kGs/cm. The final
energy of the accelerated ions Wi2 = 5 MeV/nucleon is achieved in the H-resonator,
which has the length L2 = 17 m, high voltage on each gap
E1 = 250 kV/cm, frequency f2 = 150 MHz. Focusing of the ion beam
is realized by quadrupole magnetic lenses inside the drift tube, the
gradient magnetic field
G = 7.25 kGs/cm.
|
E14-2008-77 (558.211)
Khalil A.S., Didyk A.Yu.
Disordered Zones by 100 keV Au+ Ion Irradiation in Indium Phosphide:
Direct Observations and In-situ TEM Electron-Beam-Induced Recovery
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) has been used to observe the
spatially isolated disordered zones in InP resulting from 100 keV Au ion
irradiation at room temperature which act as precursor structure for
reaching complete amorphization of the top layer at ion fluences ~ 2.5 · 1013 ions/cm2. The accumulation of damage due to the 100 keV Au
ion irradiation was described in this material using a composite theoretical
model accounting for both homogeneous and heterogeneous amorphization
processes.
|
P11-2008-80 (305.612)
Uzhinskiy А.V., Korenkov V.V.
FTS Monitoring System of EGEE/WLCG Project
Nowadays it is very important to provide a high level of Grid Services
performance and reliability. The work describes FTS monitoring system
structure and functionality (File Transfer Service, one of the gLite
services). The system was developed in the framework of the EGEE/WLCG
project. It is aimed to detect errors and nonstandard situations at data
transfer through FTS channels. The system has three components implemented
in various techniques: data mining - Perl and Shel, data storing - Mysql and
data representation - PHP and XHTML. User interface and summary reports are
shortly considered. The work has been carried out by JINR and SINP MSU
researchers in collaboration with CERN.
|
P11-2008-81 (253.804)
Nechayevskiy A.V., Korenkov V.V.
DataGrid Simulation with OptorSim Package
The work considers the main problems that are solved by
DataGrid simulation systems. OptorSim and GridSim packages are described.
The application of the OptorSim software package for DataGrid simulation is
demonstrated on an example of modelling a DataGrid segment. The obtained results are presented.
|
P11-2008-82 (105.765)
Uzhinskiy А.V., Korenkov V.V.
Statistical Analysis of Failures when Transferring Data in the Global EGEE/WLCG Infrastructure
The most frequent errors appearing while transferring files
by middleware gLite are considered. Correlation and statistical analysis of
the errors is made and main areas of their appearance are defined. Based on
the information we forward some suggestions to improve performance and reliability
of the Services. As a material for this work, we used statistic information about
errors on CERN-Tier1 and Tier1-CERN channels collected during the period from 24.03.2007 till 10.12.2007.
|
P13-2008-85 (1.096.720)
Gusakov Y.V., Grigalashvili N., Dittus F., Kekelidze G.D.,
Lysan V.M., Mjalkovskij V.V., Peshehonov V.D.,
Rusakovich N.A., Savenkov A.A., Fruadevo D., Habarova E.M.
R&D and Mass Production of the B Type Modules for the ATLAS Transition Radiation Tracker
The article considers participation of the JIN TRT team for the ATLAS
transition radiation - tracker (TRT) building together with large international
collaboration of the ATLAS Inner DetectorTRTfor the LHC. The R&D and build up
of the TRT we from 1994 up to 2007 at the Laboratory of Particle Physics, JINR,
and CERN.
|
E4-2008-87 (103.679)
Alexandrov Yu.A.
On the Possibility to Verify Multidimensional Gravity by Means of Neutrons
The possibility to verify the Newtonian gravitational law for
short distances with neutrons is discussed. Deviation from the law may be expected
in case of validity of the idea on the existence of multidimensional gravity. Within
the framework of the theoretical model related to the length of electroweak interaction
in the Born approximation expressions for the amplitudes of gravitational neutron
scattering have been obtained. Influence of the gravitational scattering on the
asymmetry (forward-backward) of the neutron scattering interacting with nuclei
at the neutron energies from ultracold ones (10-10 eV) up to several GeV has
been calculated. Analysis of the results shows that such experiments may scarcely
serve as verification of the idea of existence of multidimensional gravitation at the existing accuracy.
|
P15-2008-88 (1.001.419)
Tyukavkin A.N., Pyatkov Yu.V., Kamanin D.V., Kopatch Yu.N., Alexandrov A.A., Alexandrova I.A.,
Borzakov S.B., Voronov Yu.N., Denisov S.V., Efimov G.L., Zhuchko V.E., Kondratyev N.A.,
Kuznetsova E.A., Lavrova Yu.E., Mitrofanov S.V., Panteleev Ts., Salamatin V.S., Tsurin I.P.
Measurement of Nuclear Charges of Fission Fragments Using Big Ionization Chamber in the Frame of a Double-Armed Time-of-Flight Spectrometer
Multiparameter identification of the reaction products proved to be very
actual in studying of rare collinear multibody decays of the low excited
heavy nuclei. This work is dedicated to the method of measuring nuclear
charges of the decay products detected by high aperture ionization chamber
in the frame of a double-armed time-of-flight spectrometer. Two versions of the nuclear charge calibration procedure were worked out
using the data from the reaction 235U(nth, f). Simulation showed
that charge parameterization based on the Bohr-Willer empirical equation
used in the framework of the calibration procedure proposed here allows one to
estimate satisfactorily the fragment nuclear charge in a wide energy range.
The predicted charges for the light ions from He up to C prove to be
overestimated by approximately two charge units.
|
P14-2008-89 (178.438)
Balasoiu M., Barsov S.G., Bica D., Vekas L., Vorobyev S.I., Gritsaj K.I., Duginov V.N.,
Zhukov V.A., Komarov E.N., Koptev V.P., Kotov S.A., Mamedov T.N., Petrescu C., Shcherbakov G.V.
Study of the Properties of the Nanostructured Magnetic Systems on the Fe3O4
Basis by the  SR-Technique SR-Technique
The ferrofluid on the basis of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles
dispersed in the heavy water D2O has been investigated by the  SR-technique.
The experiment was carried out at the temperatures 26-300 K. It was observed that muon
(diamagnetic) fraction is created in the ferrofluid approximately in the same proportion
as in D2O; however, the muon spin relaxation rate is considerably higher in the
ferrofluid than in D2O. The essential frequency shift of the muon spin precession
in the ferrofluid was found. It is shown that this frequency shift of the muon spin
precession is described by the Langevin function typical for the paramagnetic. The
value of the mean field in the matter due to polarization of the magnetic nanoparticles
is determined experimentally for the first time. The nanoparticles size was estimated. SR-technique.
The experiment was carried out at the temperatures 26-300 K. It was observed that muon
(diamagnetic) fraction is created in the ferrofluid approximately in the same proportion
as in D2O; however, the muon spin relaxation rate is considerably higher in the
ferrofluid than in D2O. The essential frequency shift of the muon spin precession
in the ferrofluid was found. It is shown that this frequency shift of the muon spin
precession is described by the Langevin function typical for the paramagnetic. The
value of the mean field in the matter due to polarization of the magnetic nanoparticles
is determined experimentally for the first time. The nanoparticles size was estimated.
|
E13-2008-90 (209.915)
Batusov V., Budagov J., Khubua J., Lasseur C., Lyablin M., Russakovich N., Sissakian A., Topilin N.
Photodetector Noise Limitations of the Laser Ray Space Localization Precision
The laser ray space localization uncertainty introduced by the
noise of the laser spot registering duant photoreceiver has been studied and found to be of the order of -8 m.
|
E7-2008-91 (823.576)
Sagaidak R.N.
Fusability and Survivability in Reactions Leading to Heavy Nuclei in the Vicinity of the N=126 Shell
The production of heavy nuclei from Rn to Th around the N = 126
neutron shell in complete fusion reactions of nuclei has been considered in
а systematic way in the framework of the conventional barrier-passing
fusion model coupled with the Standard Statistical Model (SSM). Available
data on the excitation functions for fission and production of evaporation
residues obtained in very asymmetric combinations are described with these
models rather well. In the interaction of massive projectiles with heavy
target nuclei quasi-fission effects appear in the entrance reaction channel.
The quantity of the fusion probability introduced empirically has been used
to reproduce excitation functions with the same SSM parameters (fission
barriers) as those obtained in the analysis of very asymmetric combinations.
А lack of stabilization against fission around N = 126 for Th nuclei was
earlier explained with а reduced collective contribution to the level density in spherical nuclei.
However, the present analysis shows severe
inhibition for fusion, i.е., the drop in production cross sections of Th
nuclei in the vicinity of N = 126 is mainly caused by entrance channel
effects. The macroscopic component of fission barriers for nuclei involved
in а deexcitation cascade has been derived and compared with the theoretical
model predictions and available data.
|
P13-2008-92 (325.716)
Tsyganov Yu.S.
Rare Decay Events - Theoretical Aspects of Registration and Data Processing
Theoretical models describing silicon radiation detector application in
the experiments aimed at the synthesis of Super Heavy Elements in the detection of rare
alpha decays are considered. Some peculiarities of rare registration statistics associated
to the strong non-uniformity of the background signals rate, as well as formation of recoil
spectra are under consideration too. Amplitudes of spontaneous fission signals of the implanted
nuclei are presented.
|
E2-2008-93 (311.153)
Pestov I.B.
Self-Organization of Physical Fields and Spin
The subject of the present investigation is the laws of intrinsic
self-organization of fundamental physical fields. In the framework of the Theory
of Self-Organization the geometrical and physical nature of spin phenomena is uncovered.
The key points are spin symmetry (the fundamental realization of the concept of geometrical
internal symmetry) and the spinning field (space of defining representation of spin symmetry).
It is shown that the essence of spin is the bipolar structure of spin symmetry induced by the
gravitational potentials. The bipolar structure provides natural violation of spin symmetry
and leads to spinstatics (theory of spinning field outside the time) and spindynamics. The
equations of spinstatics and spindynamics are derived. It is shown that Sommerfeld's formula
can be derived from the equations of spindynamics and hence the correspondence principle is
valid. This means that the Theory of Self-Organization provides the new understanding of spin phenomena.
|
E15-2008-94 (1.262.436)
Majerle M., Adam J.,  aloun P., Gustov S.A., Henzl V., Henzlov aloun P., Gustov S.A., Henzl V., Henzlov D., Kalinnikov V.G.,
Krivopustov M.I., Kr D., Kalinnikov V.G.,
Krivopustov M.I., Kr sa A., Kr sa A., Kr  ek F., Kugler A., Mirokhin I.V., Solnyshkin A.A.,
Tsoupko-Sitnikov V.M., Wagner V. ek F., Kugler A., Mirokhin I.V., Solnyshkin A.A.,
Tsoupko-Sitnikov V.M., Wagner V.
Spallation Experiment on Thick Lead Target: Analysis of Experimental Data with Monte Carlo Codes
The Monte Carlo codes MCNPX and FLUKA were used to analyze the experiment
realized at the Laboratory of Nuclear Problems of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research
(Dubna) in December 2003. A 660 MeV proton beam was directed to a thick lead target producing
spallation neutrons, which were probed at different places around the target with small
activation detectors. The codes were used to study the systematic uncertainties and to
predict the experimental results. Several spallation models included in MCNPX and FLUKA
were checked against each other and the experiment. Both codes described successfully
most of the experimental results.
|
E15-2008-95 (288.743)
Karamian S.A.
Fission-to-Spallation Ratio and Fission Dynamics Manifestation
Fission of highly excited nuclei is affected by the viscous character
of the system motion in deformation coordinates for very heavy nuclei with Z  90.
The long-time scale fission was proved for such systems formed in heavy-ion induced reactions.
The overdamped diabatic motion may influence also fission of the spallation-residue products
in reactions with protons at intermediate energy. The experimental results on fission-to-spallation
ratio are analyzed and the evidences for the long-time scale fission are found in the fission
excitation functions for medium-mass targets with Z = 70-75. 90.
The long-time scale fission was proved for such systems formed in heavy-ion induced reactions.
The overdamped diabatic motion may influence also fission of the spallation-residue products
in reactions with protons at intermediate energy. The experimental results on fission-to-spallation
ratio are analyzed and the evidences for the long-time scale fission are found in the fission
excitation functions for medium-mass targets with Z = 70-75.
|
P18-2008-96 (586.296)
Pankratova Yu.S., Frontasyeva M.V., Pavlov S.S., Zelnitchenko N.I.
Atmospheric Pollution in the Republic of Udmurtia - Estimations Based on Moss Analysis
For the first time, air pollution studies in the Republic of Udmurtia
were carried out using the moss biomonitoring technique and neutron activation analysis.
Statistical and graphical methods of analysis were used to identify and characterize
the main sources of air pollution. The results obtained were compared to similar data
from different areas of Russia.
|
P19-2008-97 (193.490)
Stepanova A.N., Koltovaya N.A.
Induction of DNA Deletions after UV-Light Irradiation in Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
We study mutagenic action of such a damaging agent as UV light,
which can lead to DNA double-strand breaks (DSB). DNA deletions and gross
rearrangements occur in process of DSB repair. We show that UV light induces
deletion and rearrangement very efficiently. Analysis of efficacy of different
types of repair shows that cell tries to repair DSBs with a combination of both
homologous recombination (HR) and nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) if available
and that DSB repair by HR is more effective than by NHEJ in growing culture of haploid yeast.
|
E1-2008-98 (450.449)
Pozdnyakov V.N., Vertogradova Yu.L.
The Heavy-Ion Physics Programme with the ATLAS Detector
The CERN LHC collider will operate with lead ions at 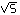 of 5.5 TeV/nucleon.
The ATLAS detector, designed to study high-pT physics in pp mode of the LHC,
has potential to study ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions in a full range
of observables characterizing the extremely dense matter and the formation of
a quark-gluon plasma. The ATLAS physics programme includes global event measurements
(particle multiplicities, transverse momentum), suppression of heavy-quarkonia
production, jet quenching and study of ultraperipheral collisions. of 5.5 TeV/nucleon.
The ATLAS detector, designed to study high-pT physics in pp mode of the LHC,
has potential to study ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions in a full range
of observables characterizing the extremely dense matter and the formation of
a quark-gluon plasma. The ATLAS physics programme includes global event measurements
(particle multiplicities, transverse momentum), suppression of heavy-quarkonia
production, jet quenching and study of ultraperipheral collisions.
|
E15-2008-99 (470.773)
Bogdanova L.N., Bom V.R., Demin A.M., Demin D.L., van Eijk C.W.E.,
Filchagin S.V., Filchenkov V.V., Grafov N.N., Grishechkin S.K., Gritsaj K.I., Konin A.D.,
Kuryakin A.V., Medved' S.V., Musyaev R.K., Rudenko A.I., Tumkin D.P., Vinogradov Yu.I., Yukhimchuk A.A.,
Yukhimchuk S.A., Zinov V.G., Zlatoustovskii S.V.
Experimental Investigation of Muon Catalyzed t+t Fusion
Muon catalyzed fusion ( CF) process in tritium was
studied by the CF) process in tritium was
studied by the  CF collaboration on the muon beam of the JINR Phasotron.
The measurements were carried out with a liquid tritium target at temperature
22 K and density CF collaboration on the muon beam of the JINR Phasotron.
The measurements were carried out with a liquid tritium target at temperature
22 K and density  1.25 of liquid hydrogen density (LHD). Parameters of
the 1.25 of liquid hydrogen density (LHD). Parameters of
the  CF cycle were determined: tt CF cycle were determined: tt -muonic molecule formation rate
ltt -muonic molecule formation rate
ltt =2.84 (0.32) =2.84 (0.32)  s-1, tt fusion reaction rate
lf=15.6 (2.0) s-1, tt fusion reaction rate
lf=15.6 (2.0)  s-1 and probability of muon sticking
to helium s-1 and probability of muon sticking
to helium 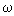 tt=13.9 (1.5)%. The results agree with those ones
earlier obtained by other groups, however, better accuracy was achieved due
to our unique experimental method. tt=13.9 (1.5)%. The results agree with those ones
earlier obtained by other groups, however, better accuracy was achieved due
to our unique experimental method.
|
P1-2008-100 (1.025.733)
Troyan Yu.A., Jerusalimova A.P., Beyaeva A.V., Troyana A.Yu., Plekhanova E.B., Arakelian S.G.
The Search and Study of Low-Mass Scalar Mesons at the Impulse of Neutron Beam
Pn =(5.20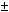 0.12) GeV/c in the Reaction i>np 0.12) GeV/c in the Reaction i>np np np 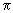 + +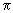 - -
Using irradiation of 1 m HBC LHE JINR by quasimonochromatic neutron
beam with impulse Pn =(5.20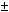 0.12) GeV/c which was produced after acceleration
of deuterons in the synchrophasotron LHE JINR, 25650 events of reaction
np 0.12) GeV/c which was produced after acceleration
of deuterons in the synchrophasotron LHE JINR, 25650 events of reaction
np np np 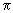 + +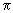 - were selected. After supplementary sorting out
events in which cos - were selected. After supplementary sorting out
events in which cos  p* >0 in the effective mass spectrum of p* >0 in the effective mass spectrum of
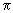 + +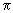 --combinations there were found out nine peculiarities at masses
350, 408, 489, 579, 676, 762, 878, 1036, 1170 MeV/c2 and with experimental
widths not more than several tens of MeV/c2.
The resonance effects are significantly increased after using additional criterion -
balance of the summary of the longitudinal impulses of --combinations there were found out nine peculiarities at masses
350, 408, 489, 579, 676, 762, 878, 1036, 1170 MeV/c2 and with experimental
widths not more than several tens of MeV/c2.
The resonance effects are significantly increased after using additional criterion -
balance of the summary of the longitudinal impulses of 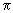 +and +and 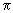 - mesons
in general c.m.s. of reaction. By these conditions values of standard derivations from
background are more than 5 for all peculiarities.
The direct measurement of the spins of resonances was carried out. Also, other
quantum numbers were obtained. All these peculiarities have IG (JPC)=0+(0++).
In this way, the sequence of scalar-izoscalar resonances f0( - mesons
in general c.m.s. of reaction. By these conditions values of standard derivations from
background are more than 5 for all peculiarities.
The direct measurement of the spins of resonances was carried out. Also, other
quantum numbers were obtained. All these peculiarities have IG (JPC)=0+(0++).
In this way, the sequence of scalar-izoscalar resonances f0(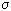 0) with
masses in the range M 0) with
masses in the range M  1200 MeV/c2 is seen. The information about these
resonances was absent in literature.
The phenomenological dependence of mass of resonance on its number was found.
This dependence covers not only resonances shown in this paper but also all
the resonances with quantum numbers of f0( 1200 MeV/c2 is seen. The information about these
resonances was absent in literature.
The phenomenological dependence of mass of resonance on its number was found.
This dependence covers not only resonances shown in this paper but also all
the resonances with quantum numbers of f0(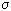 0) mesons presented in PDG. 0) mesons presented in PDG.
|
P9-2008-102 (344.899)
Efremov A., Bogomolov S., Kochagov O., Loginov V., Kazarinov N.
The Use of the Ohmic Heated Sheet in Combination with the ECR Ion Source for the Production of the Ca Ion Beam
The production of intense accelerated 48Ca ion beams is the key problem
in the experiments on the synthesis of new super heavy nuclei. For this
purpose in the FLNR (JINR) an ECR ion source is used at the U-400 cyclotron.
The combination of a microoven with a hot tantalum sheet inside the
discharge chamber allowed the production of the intense 48Ca5+ ion
beam at the 48Ca consumption of about 0.5 mg/h. In this case the
tantalum sheet is heated by microwaves and plasma electrons. The microwave
power of up to 400 W is required to heat the sheet to the temperature of
about 500 ° C. To decrease the required microwave power a new sheet with
a direct ohmic heating was designed. The present paper describes the method,
technique and preliminary experimental results on the production of the Ca
ion beam.
|
P11-2008-103 (366.496)
Amirkhanov I.V., Muzafarov D.Z., Sarker N.R., Sarhadov I., Sharipov Z.A.
Investigation of Solutions of Boundary Problems for Singular-Perturbed Differential
Equation of Fourth Order in a Field of Coulomb Potential
In the paper an algorithm to find eigenvalues and
eigenfunctions for one boundary problem for the equation of 4th order with
a small parameter at the highest derivative with Coulomb potential is proposed.
The algorithm is implemented using the symbolic calculations MAPLE. At   0,
this equation converts to the Schrodinger equation. The investigations of
eigenvalues and eigenfunctions with different values of 0,
this equation converts to the Schrodinger equation. The investigations of
eigenvalues and eigenfunctions with different values of  have been conducted.
In the fixed value of have been conducted.
In the fixed value of  two types of solutions have been found. At two types of solutions have been found. At   0,
one of these solutions converts to the solution of the Schrodinger equation, and
the other comes into boundary layer. 0,
one of these solutions converts to the solution of the Schrodinger equation, and
the other comes into boundary layer.
|
E11-2008-104 (638.555)
Yuldashev O.I., Yuldasheva M.B.
3D Finite Elements with Harmonic Basis Functions for Approximations of High Orde
As is known, most wide-spread finite elements are defined as a cell with
basis functions. In the present paper for such cells as tetrahedron, cube, rectangular prism,
etc., the methods of production of harmonic basis functions with
approximation of high order have been developed. In particular, the recursion relations
for calculation of the basis functions and the algorithm of their production are presented.
The conditions on transformations of coordinates keeping the harmonicity property
of the basis functions are also considered.
The distinctive peculiarities of obtained finite elements are absence of inner nodes and
possibility of adaptive condensation of nodes on a cell boundary.
For tetrahedrons and rectangular prisms the constructed basis functions exactly approximate
the harmonic polynomials of the second, third, fourth and fifth orders.
The proposed finite elements may be used for problems of interpolation and
integration of harmonic functions and also for solving the boundary value problems
with Laplace and Poisson equations in scalar and vector cases by means of projective
numerical methods. The examples of hp-interpolation of dipole magnetic
fields with high accuracy are given. The approximations obtained as a result of
the interpolation satisfy the vector Laplacian with computer accuracy. In order to
construct the approximations a smaller number of nodes is required in comparison
with the usual Lagrange finite elements.
|
P19-2008-105 (716.030)
Belov O.V., Krasavin E.A., Parkhomenko A.Yu.
Mathematical Model of Induced Mutagenesis in Bacteria
Escherichia coli under Ultraviolet Irradiation
The mathematical model of mutational process in bacteria
Escherichia coli induced by ultraviolet radiation is developed.
Dynamics of the basic protein complexes of the E. coli SOS-response
system is investigated. The probability of mutations occurring during translesion-synthesis is estimated.
|
P2-2008-107 (617.358)
Shirkov D.V.
The Bogoliubov Renorm-Group
This is a separate publication of the Supplement to volume X of Сollected Works (in 12 volumes)
by N.N. Bogoliubov devoted to his 100th birthday.
The paper contains a propaedeutic review of the renormalization group fundamentals in the form
ascending to Marius Sophus Lie treatise of the end of the 19th century. This standpoint treats
renormalization group as a continuous Lie group of finite transformations, with the underlying symmetry
being an exact symmetry of a partial solution. Just this interpretation was put by Bogoliubov as a
base of his papers of the mid-1950s. That is the reason that we use the name "the Bogoliubov Renorm-Group".
Such an approach releases the renormalization group from any association with subtracting ultraviolet
divergencies. In turn, it lightens the appreciation of foundations of the renormalization group and of the
renormalization group method in quantum theory. At the same time it helps to realize its affinity
and differences with approximate Wilson's semigroup in the theory of critical phenomena and with
some other constructions that employ the related terminology. We give a few
simple examples from the classical physics.
The last Section contains an overview of three recently (1980s-1990s) devised fields of application
of the Bogoliubov Renorm-Group:
- mass-dependent renorm-group in the threshold vicinity in the context of the Standard Model,
- Analytic Perturbation Theory in Quantum Chromodynamics free of unphysical singularities, and
- the "Renorm-Group Symmetries" method for improvement of boundary value problem solution in mathematical
physics.
|
E1-2008-108 (1.774.824)
Lyubushkin V.V., Popov B.A.
A Study of Quasi-Elastic Muon (Anti)Neutrino Scattering in the NOMAD Experiment
We have studied the muon neutrino and antineutrino quasi-elastic (QEL)
scattering reactions
(  n n  - p and - p and
  p p  +n)
using a set of experimental data collected by the NOMAD collaboration.
We have performed measurements of the cross section of these processes on
a nuclear target (mainly carbon) normalizing it to the total +n)
using a set of experimental data collected by the NOMAD collaboration.
We have performed measurements of the cross section of these processes on
a nuclear target (mainly carbon) normalizing it to the total 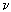  ( (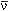  )
charged current cross section. The results for the flux averaged QEL cross
sections in the (anti)neutrino energy interval 3-100 GeV are
< )
charged current cross section. The results for the flux averaged QEL cross
sections in the (anti)neutrino energy interval 3-100 GeV are
<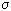 gel> gel>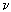  = (0.92 = (0.92 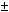 0.02 (stat.) 0.02 (stat.) 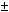 0.06 (syst.)) · 10-38 cm2
and < 0.06 (syst.)) · 10-38 cm2
and <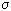 gel> gel>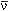  =
(0.81 =
(0.81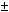 0.05 (stat.) 0.05 (stat.) 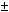 0.08 (syst.)
· 10-38 cm2 for neutrino and antineutrino, respectively.
The axial mass parameter MA was extracted from the measured quasi-elastic
neutrino cross section. The corresponding result is MA = 1.05 0.08 (syst.)
· 10-38 cm2 for neutrino and antineutrino, respectively.
The axial mass parameter MA was extracted from the measured quasi-elastic
neutrino cross section. The corresponding result is MA = 1.05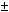 0.02 (stat.) 0.02 (stat.) 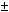 0.06 (syst.) GeV.
It is consistent with the axial mass values recalculated
from the antineutrino cross section and extracted from the pure Q2 shape analysis of
the high purity sample of 0.06 (syst.) GeV.
It is consistent with the axial mass values recalculated
from the antineutrino cross section and extracted from the pure Q2 shape analysis of
the high purity sample of 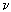  quasi-elastic 2-track events, but has smaller
systematic error and should be quoted as the main result of this work. The measured
MA is found to be in good agreement with the world average value obtained in the
previous deuterium filled bubble chamber experiments. These results do not support
MA measurements published recently by the K2K and MiniBooNE collaborations, which
reported somewhat larger values, which are however compatible with our results within
their large errors. quasi-elastic 2-track events, but has smaller
systematic error and should be quoted as the main result of this work. The measured
MA is found to be in good agreement with the world average value obtained in the
previous deuterium filled bubble chamber experiments. These results do not support
MA measurements published recently by the K2K and MiniBooNE collaborations, which
reported somewhat larger values, which are however compatible with our results within
their large errors.
|
E13-2008-109 (1.641.787)
Malkov I., Perevozchikov V., Rybakov V., Zhigalov V.,
Budagov Yu., Sabirov B., Sissakian A., Shirkov G., Sukhanova A.
Investigation of the Possibility of Producing the Bimetallic Tube Transition
Element by Explosion Welding for the Cryomodule of the International Linear Collider
The results of the investigation of the possibility of producing the
bimetallic tube transition element for the cryomodule of the International Linear Collider
(ILC) by explosion welding at the Russian Federal Nuclear Center — VNIIEF (Sarov) are presented.
Three options of the bimetallic transition tube were made of titanium and type 316 stainless steel
produced by different manufacturers.
The quality of the titanium–stainless steel welded joint was checked by the following inspection
methods: measurement of leak rate; determination of strength; metallographic analysis.
It is shown that the quality of the welded joint of the bimetallic tube billet is satisfactory.
All welded joints tested before and after cooling in liquid nitrogen within ~ 10 min show good
leakproof (< 1·10-9 atm·cm3/s). Shearing strength of the welded joint is  sh sh 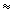 500 MPa. Macrodefects,
such as cracks, spills, and peelings, were not found in the welded joints. Small and evenly distributed
microdefects (interstices, intermetallides) not forming big aggregations do not influence the working
capacity of the welded joints. 500 MPa. Macrodefects,
such as cracks, spills, and peelings, were not found in the welded joints. Small and evenly distributed
microdefects (interstices, intermetallides) not forming big aggregations do not influence the working
capacity of the welded joints.
|
E13-2008-110 (805.155)
Budagov J., Sabirov B., Sissakian A., Shirkov G., Sukhanova A.,
Malkov I., Perevozchikov V., Rybakov V., Zhigalov V.,
Basti A., Bedeschi F., Frasconi F., Linari S., Kephart R., Nagaitsev S.
Leak Rate Measurements on Bimetallic Transition Samples for ILC Cryomodules
The results of leak test of bimetallic (titanium-stainless steel)
transition elements produced by explosion welding are presented. Vacuum and high-pressure
tests of the sample for leakage were carried out at room temperature and liquid nitrogen
temperature. Similar tests were also carried out under thermal cycling conditions.
|
E13-2008-111 (884.617)
Budagov J., Budagov J., Sabirov B., Sissakian A., Shirkov G., Sukhanova A.,
Malkov I., Perevozchikov V., Rybakov V., Zhigalov V.,
Basti A., Bedeschi F., Frasconi F., Linari S., Kephart R., Nagaitsev S.
Characterization Measurements of Ti–SS Bimetallic Transition Joint Samples
A small set of bimetallic tubes has been investigated for
the purpose to determine characteristics of samples at different conditions
of tests for more statistics. Nine bimetallic samples have been manufactured
at the Russian Federal Nuclear Center — VNIIEF (Sarov, Russia) using explosion
technology for welding titanium and stainless steel tubes. During the tests eight
samples have shown an excellent behavior. This result is very good and we believe
that these samples can be used for the construction of the cavity vessels.
A preliminary measurement on the residual magnetic moment around junction line
between the two materials has been carried out.
|
P2-2008-115 (131.413)
Kashukeev N.T.
On One Inference from the Uncertainty Principle to Gravitation
The uncertainty relation Dp Dx
 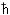 /2
applied to the Universe of the size R /2
applied to the Universe of the size R 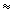 1028 cm and to a particle
momentum Dp= 1028 cm and to a particle
momentum Dp= c leads to a minimal possible particle mass of c leads to a minimal possible particle mass of
 1.8·10-66 g. The assumption is made that such minimal
mass particles are responsible for the gravitational interaction. 1.8·10-66 g. The assumption is made that such minimal
mass particles are responsible for the gravitational interaction.
|
P13-2008-116 (370.541)
Busykin O.G., Kazakov A.V., Kulagin E.N., Kulikov S.A., Shabalin D.E., Shabalin E.P.
On Pneumatic Conveying of Solid Beads of a Cold Neutron Moderator
Results of numerical modeling of aerodymamics and movement
of an ideal smooth single ball conveying pneumatically inside a cylindrical
pipe, including aerodynamical forces and angular momentum coefficients, are
presented. Ratio of a diameter of the ball to that of the pipe was as much
as 0.3. Analytic solutions of a transport equation using calculated coefficients
were derived as well. Experiments on a simulating conveying pipe have approved
analytical approach for movement of a spherical bead through a cylindrical pipe
but for initial stage of acceleration where speed of a ball is up to 30-40 %
of an averaged gas velocity. At higher speed of a ball, nonregularity of its movement,
that is, alternation of acceleration and deceleration, appears to be inevitable.
Reason of it is roughness of pipe walls and deviation of bead shape from spherical one.
|
P19-2008-117 (370.441)
Feldman T.B., Kholmurodov Kh.T., Ostrovsky M.A., Khrenova M.G., Nemukhin A.V.
Studies on Conformational States of the Chromophore Group, 11-cis-Retinal,
in Rhodopsin by Computer Molecular Simulation Methods
Based on computer simulation methods a comparative study of
molecular dynamics of rhodopsin, which contains a chromophore (11-cis-retinal)
group, and a free opsin has been performed. Molecular dynamics has been traced up
within 3 ns time interval; thereby 3 · 106 discrete conformational states
of rhodopsin and opsin were compared and analyzed. It is demonstrated that the presence
of a light absorbing group (11-cis-retinal) in opsin's chromophore pocket has a
considerable influence on the protein neighborhood, surrounding of 11-cis-retinal
from beta-ionone ring region, as well as on the distant (cytoplasmic and extracellular)
regions. From the simulation results we discuss the molecular mechanism that assumes
rhodopsin as a G-protein coupled receptor in the inactivated state functioning as
an efficient ligand antagonist.
|
E15-2008-118 (1.147.650)
Adam J., Katovsk K., Majerle M., Krivopustov M.I., Kumar V., Manish Sharma,
Chitra Bhatia, Solnyshkin A.A., Tsoupko-Sitnikov V.M. K., Majerle M., Krivopustov M.I., Kumar V., Manish Sharma,
Chitra Bhatia, Solnyshkin A.A., Tsoupko-Sitnikov V.M.
Transmutation of Th and U with Neutrons
Produced in Pb Target and U-Blanket System
by Relativistic Deuterons
Lead target and uranium blanket setup called "Energy
plus Transmutation" was irradiated by 1.6 GeV deuteron beam from the
Nuclotron accelerator at the Laboratory of High Energies of Joint Institute for
Nuclear Research (Dubna). Neutrons generated by spallation
reactions of deuterons with lead target interact with subcritical uranium
blanket. In the neutron field outside the blanket radioactive uranium and
thorium samples were irradiated. Reaction rate of some residual nuclei
determined using the method of gamma-spectrometry in the experiment is used
to calculate the transmutation power of the setup. Experimental results are
compared with the Monte Carlo calculation performed by the MCNPX 2.6.C code
and with some results of the TARC experiment.
|
E18-2008-119 (456.618)
Baljinnyam N., Belov A.G., Ganbold G., Gerbish Sh., Maslov O.D., Shvetsov V.N.
Possibility of Some Radionuclides Production Using High Energy Electron Bremsstrahlung
The method of some radionuclides production using high energy
bremsstrahlung of electron accelerators and determination of photonuclear reaction
yield and specific activitiеs for some radioinuclides is described. Photonuclear
reaction yield and specific activitiеs for some radioinuclides are determined for
117mSn, 111In and 195mPt.
Based on the experimental data obtained at low energy (Ee- < 30 MeV)
electron accelerators as well as the microtron MT-25 (FLNR, JINR) with the power 0.5 kW,
photonuclear reaction yields are estimated for some radionuclides for the linear electron
accelerator (Ee- = 75 МeV) of the IREN facility (FLNP, JINR) at irradiation of high
purity platinum and tin metals.
|
E18-2008-120 (606.027)
Gerbish Sh., Baljinnyam N., Ganbold G., Ganchimeg G.
Determination of Major and Minor Elements in Sediments of the Central and Northern Mongolian Rivers Using INAA
The sediment samples from rivers of the central and northern
part of Mongolia were studied and the concentration of 41 elements
(Na, Mg, Cl, K, Ca, Al, Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Br, Sr,
Rb, Zr, Nb, Sb, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Tb, Dy, Tm, Hf, Ta, W, Au, Hg, Th, U)
was determined by instrumental neutron activation analysis using epithermal
neutrons (INAA) at the IBR-2 reactor (FLNP, JINR, Dubna). The obtained results
of heavy metals and other trace elements in these samples were compared with
the reference materials and other clean area data.
|
E14-2008-123 (329.504)
Balasoiu M., Craus M.L., Plestil J., Haramus V., Erhan R., Lozovan M., Kuklin A.I., Bica I.
Microstructure of Magnetite Doped Elastomers Investigated by SAXS and SANS
We present some recent results on the SAXS and SANS investigations of
the magnetic elastomers. Samples were obtained by polymerizing dimethylsiloxane with
Fe3O4 ferrofluid in a magnetic field and without magnetic field and characterized by
XRD, SANS and SAXS. The SAXS maximum at large angles, obtained from magnetic elastomers,
was fitted by using a Pseudo-Voigt function. It was found that the Fe3O4 particles
lead to a change of the local structure of elastomer, meaning the decrease of the quasi-crystalline
phase and of the micro-strains induced in the matrix. The average particle size obtained
from SANS measurements agrees well with the average particle size determined by XRD and
SAXS analysis. The splitting of the SANS intensity owing to an additional scattering in
zero field reflects the existence of magnetic correlations inside the Q region of
0.005 < Q < 0.02  -1. -1.
|
E2-2008-125 (1.067.524)
Zborovsk I., Tokarev M.V. I., Tokarev M.V.
New Properties of z-Scaling: Flavor Independence and Saturation at Low z
Experimental ISR, RHIC, and Tevatron data on inclusive cross
sections of particles produced in high energy proton-(anti)proton collisions
are analyzed in the framework of z-scaling. New features of the scaling
function y(z) are established. These are flavor independence of y(z)
including particles with heavy flavor content and saturation at low z. Flavor
independence means that the shape of the scaling function y(z) is the same
for different hadron species. Saturation corresponds to flattening of y(z)
for low z< 0.1. Relations of model parameters used in data z-presentation with
some thermodynamical quantities (entropy, specific heat, temperature) are discussed.
It is shown that behavior of particle spectra at low z is controlled by a parameter
c interpreted as specific heat of the created medium associated with production
of the inclusive particle. The saturation regime of y(z) observed at low z is
assumed to be preferable in searching for phase transitions of hadron matter and for
study of nonperturbative QCD in high energy proton-(anti)proton collisions at U70,
RHIC, Tevatron, and LHC.
|
E3-2008-134 (271.701)
Sukhovoj A.M., Khitrov V.A.
Level Density, Radiative Strength Functions from the nth, 2g Reaction
and Main Properties of the 96Mo Nucleus
The data published on two-step cascade intensities to 12 final levels
of 96Mo were approximated for different energies of excitations and dipole
primary E1- and M1-transitions by a set of different random dependencies of
the level density and strength functions. The averaged values of these parameters
of gamma-decay well correspond to main dependencies revealed by now from analogous
experiments for 42 nuclei from the mass region 40  A A  200.
And they do not correspond to the existing ideas of the cascade gamma-decay
parameters of compound-nuclei with high level density. 200.
And they do not correspond to the existing ideas of the cascade gamma-decay
parameters of compound-nuclei with high level density.
|
E16-2008-136 (683.325)
Cata-Danil G., Paraipan M., Timoshenko G.
Ridge Filter Design for Carbon Therapy
The design of a ridge filter intended for forming the uniform
spread-out Bragg peak within a tumour at carbon therapy is described.
The computation of the ridge filter shape was carried out by an analytical
algorithm and tested by MC simulation (GEANT4 code). Two kinds of the ridge
filter were considered: stationary and movable. The influence on a ridge filter
shape of the carbon beam energy and the type of relative biological effectiveness
dependence on the carbon ion linear energy transfer in tissue were examined.
|
P13-2008-137 (514.663)
Ivanov M.P., Astabatian R.A., Gulbekian G.G., Demekhina N.A., Kulko A.A.,
Lukyanov S.M., Penionzhkevich Yu.E., Revenko R.V., Skobelev N.K., Smirnov V.I., Sobolev Yu.G., Testov D.A.
Obtaining of Monochromatic Beams of Accelerated 6He
Ions with Energies Close to Coulomb Barrier at the Accelerator Complex DRIBs (JINR)
Two methods for obtaining monochromatic beams of accelerated 6He
ions with energies close to Coulomb barrier at the accelerator complex DRIBs (JINR)
are described. In the first method the magnetic spectrometer MSP-144 was used as
monochromator of 6He particles beam after energy degrader. The energy resolution
(500 keV) was determined from linear size (18 mm) of the target along the focal plane.
In the second method the especially designed probe was used for investigation of
nuclear reactions with accelerated 6He ions without intensity loss on internal
beam of postaccelerator (U400 cyclotron) of DRIBs (JINR) complex. The 6He
particle beam of required energy with an energy resolution not worse than 150 keV
on the target was obtained.
|
E3-2008-138 (572.518)
Balasoiu M., Anitas E.M., Bica I., Osipov V.A.,
Orelovich O.L., Savu D., Savu S., Erhan R., Kuklin A.I.
SANS of Interacting Magnetic Micro-Sized Fe Particles in a Stomaflex Creme Polymer Matrix
The investigations results obtained from small-angle neutron
scattering on magnetic elastomers polymerized with and without magnetic
field at 25, 50 and 75 % mass concentration of Fe particles with a mean
radius of 2.09  m inside a Stomaflex creme polymer matrix have been
reported. The magnetic field used in polymerization process is 156.5 mT.
The profiles of the curves from SANS have a similar behavior for each concentration,
showing that for these sizes of particles and polymerization process at 156.5 mT,
the microstructure of magnetic elastomers is the same in the q-range of
0.006-0.1 m inside a Stomaflex creme polymer matrix have been
reported. The magnetic field used in polymerization process is 156.5 mT.
The profiles of the curves from SANS have a similar behavior for each concentration,
showing that for these sizes of particles and polymerization process at 156.5 mT,
the microstructure of magnetic elastomers is the same in the q-range of
0.006-0.1 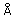 -1, and scattering intensities increase proportionally
with increasing the mass concentration of Fe particles. -1, and scattering intensities increase proportionally
with increasing the mass concentration of Fe particles.
|
E3-2008-139 (205.816)
Pokotilovski Yu.N., Novopoltsev M.I., Geltenbort P.
Test of the Fast Thin-Film Ferromagnetic Shutters for Ultracold Neutrons
Test of thin-film ferromagnetic shutters of two types for ultracold neutrons
has been performed. The first type is based on neutron reflection from the sequence
of successively placed thin ferromagnetic layers with oppositely directed magnetization.
The second one is based on neutron refraction in ferromagnetic foils inserted in the beam.
|
P13-2008-141 (716.303)
Batusov V., Budagov J., Leitner R., Lyabin M., Miralles L., Nessi M., Proudfoot J., Russakovich N., Sissakian A.,
Topilin N., Khubua J.,
Enrike A., Romanov V.
The Modular Nuclear Absorber of the ATLAS Hadron Calorimeter
(The experience of controlled assembly on the ground and in the pit)
The Hadron Calorimeter of the spectrometric complex ATLAS represents
a principal part of the whole setup. In the article the developed concept and methods
of the controlled assembly of the steel nuclear absorber of the calorimeter are described,
which made possible the calorimeter assembly of the surface and the underground
experimental pit following the project tolerances.
|
P11-2008-142 (343.135)
Melemov H.T., Boyadjiev T.L.
Spline-Collocation Scheme of High Order of Accuracy for Systems of Ordinary Differential Equations
In this paper we propose spline-collocation scheme for solving
linear boundary value problems for systems of ODE's of the second order.
We discuss the case when the system is given on the embedded intervals too.
For smooth enough solutions the scheme precision on uniform grids is O(h4).
The scheme can be easily generalized on discontinuous problems without violation
of the structure of the algebraic system. The scheme can be applied for solving
numerous nonlinear physical problems. As a concrete example we consider the problem
for static distributions of magnetic flux in a system of two magnetically coupled
long Josephson junctions with different layer lengths.
|
E11-2008-143 (329.779)
Melemov H.T., Boyadjiev T.L.
Numerical Solution of a Class of Boundary Value Problems Arising in the Physics of Josephson Junctions
In this paper we propose a method of numerical solution of non-linear
boundary value problems for systems of ODEs given on the embedded intervals.
The algorithm is based on the continuous analog of Newton method coupled with
spline-collocation scheme of fourth order of accuracy.
Demonstrative examples of similar problems take place in physics of stacked
Josephson junctions with different layers lengths. As a concrete example we consider
the problem of calculating the possible distributions of magnetic flux in a system
of two magnetically coupled long Josephson junctions. The influence of length ratio
on the main physical properties of basic bound states is investigated numerically.
The existence of bifurcations by change of the lengths of the layers for some couples of solutions has been proved.
|
E7-2008-144 (237.536)
Tsyganov Yu.S.
Active Correlations Technique: Schmidt Equation with Partially Free Order
A key question relating to the discovery of a new nuclide
is the probability that the observed event sequence is due to a random correlation
of unrelated events. The magnitude of this probability allows experimenters to
judge the validity of the interpretation, and is a necessary argument for or
against such a discovery. In the present paper K.H.Schmidt equation with
partially free order is considered in the form to correspond to the "active correlations"
technique application in heavy-ion-induced nuclear reactions.
|
P13-2008-145 (449.184)
Pyszniak K., Turek M., Drozdziel A., Sielanko J., Maczka D., Vaganov Yu.A., Yushkievich Yu.V.
The Facility for Studying the Ion Sputtering by Bombardment with Medium Energy Ion Beams
The design of the experimental facility for studying the
ion sputtering process of solids by bombardment with medium energy ion beams
is described. The facility underwent a number of experimental tests and computer
simulations both for the whole system and separate units. A brief review of these tests is presented.
|
E4-2008-146 (286.519)
Kartavtsev O.I., Malykh A.V., Sofianos S.A.
Bound States and Scattering Lengths of Three Two-Component Particles
with Zero-Range Interactions under One-Dimensional Confinement
The universal three-body dynamics in ultracold binary gases
confined to one-dimensional motion is studied. The three-body binding
energies and the (2 + 1)-scattering lengths are calculated for two
identical particles of mass m and a different one of mass m/m1,
between which interactions are described in the low-energy limit by
zero-range potentials. The critical values of the mass ratio m/m1,
at which the three-body states arise and the (2 + 1)-scattering length
equals zero, are determined both for zero and infinite interaction strength
l1 of the identical particles. A number of exact results are
enlisted and asymptotic dependences both for m/m1   and
l1
and
l1  - - are derived. Combining the numerical and
analytical results, a schematic diagram showing the number of the
three-body bound states and the sign of the (2 + 1)-scattering length
in the plane of the mass ratio and interaction-strength ratio is deduced.
The results provide a description of the homogeneous and mixed phases of
atoms and molecules in dilute binary quantum gases.
are derived. Combining the numerical and
analytical results, a schematic diagram showing the number of the
three-body bound states and the sign of the (2 + 1)-scattering length
in the plane of the mass ratio and interaction-strength ratio is deduced.
The results provide a description of the homogeneous and mixed phases of
atoms and molecules in dilute binary quantum gases.
|
P7-2008-147 (705.966)
Penionzhkevich Yu.E.
Peculiarities of Nuclear Reactions Induced by 6He, 6,7Li Nuclei near Coulomb Barrier Energy
Experimental excitation functions are presented for complete
fusion and transfer reactions in the interaction of 6He and 6Li with
206Pb, 209Bi and Pt targets. The data on fusion in the 6He induced
reactions at energies close to the Coulomb barrier differ from predictions
within the framework of the statistical model for compound nuclei decay.
For these exit channels a strong enhancement has been observed. Enhancement
of the cross section for neutron transfer (6He beam) and deuteron transfer
(6Li beam) reactions is observed at deep subbarrier energies. The results
are discussed from the point of view of how the nuclear cluster structure
influences the probability of interaction at near barrier energies.
|
P1-2008-148 (786.736)
Glagolev V.V., Martinska G., Musinski J.
Space Correlations in Pionless Interactions of Light Nuclei with Protons
In the present paper pionless break-up reactions of deuterium
and helium nuclei are considered. Space correlations of secondary particles
and their connection to elastic scattering are experimentally investigated.
Therefore "the inverse problem" - synthesis of light nuclei is discussed.
|
P11-2008-149 (807.191)
Akishin P.G., Sapozhnikov A.A., Fisher Z.Je., Shnicer P.B.
Automatic 3D Mesh Generator
A 3D finite elements mesh generator based on the Mapping
approach is described. In order to improve the quality of the mesh generation
a special standard subdividing elements library is used for mesh refinement.
A user-friendly interface for defining the input geometry is built. A set of
tools to describe the curvature of standard and non-standard current windings
curvature with various cross-sections is designed. This covers also the currently
requested coil windings made for coaxial cables. On all stages of the mesh generation
process a visual control of the quality is available including also the final
refinement stage. The proposed generator can be used as a preprocessor for solving
a wide range of problems based on the finite elements method.
|
P10-2008-152 (685.951)
Ivanov V.V., Lebedev A.A., Lebedev S.A., Osokov G.A.
Geometry Optimization of the Transition Radiation Detector for the CBM Experiment
A description of the software for charged particles track
reconstruction and their identification by the Transition Radiation
Detector (TRD) is given in this paper. The algorithm for track reconstruction
is based on track following method together with the Kalman filter application.
An artificial neural network, which uses as input samples the particles energy
losses in the TRD layers, has been applied for electron/pion identification.
First results on the optimization of the TRD geometry with regard for efficiencies
of track reconstruction, electron identification and pion suppression are presented.
|
E17-2008-159 (172.712)
Tonchev N.S.
Finite-Size Scaling and Strong Space Anisotropy: O( ) Spin Models ) Spin Models
We present analytical results for the finite-size scaling behavior
of d-dimensional O( ) spin systems with strong space anisotropy,
described by a model Hamiltonian with interaction between spins which in the
k space has leading terms of the form ) spin systems with strong space anisotropy,
described by a model Hamiltonian with interaction between spins which in the
k space has leading terms of the form
 i=0l ai|ki|2 i=0l ai|ki|2 i.
Here ki
are pi-dimensional vectors, such that i.
Here ki
are pi-dimensional vectors, such that  i=0l pi=d, l>0,
ai i=0l pi=d, l>0,
ai  0 are some constants and 0 are some constants and 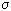 i > 0 are parameters controlling
the range of interaction. We consider systems confined to a d-dimensional layer
with the geometry Lp0( i > 0 are parameters controlling
the range of interaction. We consider systems confined to a d-dimensional layer
with the geometry Lp0(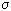 0) 0)  p1( p1(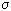 1)
... 1)
...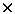  pl( pl(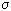 l)
and periodic boundary conditions across the finite p0 dimensions with the characteristic
length "L". It is shown that there are dimensions d between the lower and upper
critical dimensions for which the finite-size scaling behavior of the model is uniquely
determined by the parameters l)
and periodic boundary conditions across the finite p0 dimensions with the characteristic
length "L". It is shown that there are dimensions d between the lower and upper
critical dimensions for which the finite-size scaling behavior of the model is uniquely
determined by the parameters 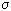 0, p0, 0, p0,  l:=1- l:=1-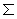 i=1l(pi/2 i=1l(pi/2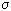 i).
Prominent examples are systems with the Lifshitz point critical behavior and/or quantum critical behavior. i).
Prominent examples are systems with the Lifshitz point critical behavior and/or quantum critical behavior.
|
E11-2008-160 (299.101)
Christov I.G., Dimova S.N., Boyadjiev T.L.
Stability and Bifurcation of the Magnetic Flux Bound States in Stacked Josephson Junctions
An effective numerical algorithm for solving the nonlinear system
of ODE describing the static distributions of the magnetic flux in N-stacked Josephson
Junctions (JJs), as well as the corresponding matrix Sturm-Liouville problem for
studying their global stability, is proposed. The developed technique gives a possibility
for detailed investigation of these multiparametric problems. We illustrate its application
to analyze the existence, stability, lack of stability and some physical characteristics
of two kinds of magnetic flux distributions in three-layered JJs.
|
E11-2008-161 (211.743)
Radev S.P., Boyadjiev T.L., Onofri F.
Mathematical Modeling of a Steady Glass Fiber Drawing Process
A spline differential numerical method is developed for studying
the non-isothermal glass fiber drawing process. The method is based on the one-dimensional
version of the equations of motion coupled by the heat transfer equation. The effects of
the temperature-dependent viscosity, gravity, surface tension and air drag, as well as
those of axial heat conduction, heat convection and radiative heat transfer are taken
into account. Numerical results for the fiber radius, axial velocity and temperature
are schown, illustrating the cooling effects of Stanton and radiation numbers.
|
P18-2008-164 (270.026)
Kovalev Yu.S., Levkovich N.V., Kuklin A.I., Apel P.Yu.
Controlling the Pore Structure in Track Membranes: The Behavior
of Surface-active Substances in Track-Etching Solutions
Surfactants are used in track-membrane etching in order to obtain
special pore geometries, for instance, with the aim of manufacturing high-productivity
membranes. To understand how the surfactants affect the track etching process,
it is necessary to know the behavior of surfactant molecules in etching solutions.
In particular, it is necessary to know how they aggregate in track-etching solutions.
We present here the results of our investigations of the micelle formation for the dodecyl
sulfophenoxy benzene sulfonate and nonyl benzene deca ethyleneoxide (NBDEO) in neutral and
alkaline solutions of electrolytes. The measurements are performed using the method of
Small-Angle Neutron Scattering (SANS). We found that the micelles formed in etching solutions
are cylindrical (elliptical) in shape. We also study the influence of the surfactant
concentration and of the type of added electrolytes on the characteristic micelle sizes.
We end the paper by discussing how the obtained data is related to the geometry and dynamics
of "track" nanopores etching in surfactant-enhanced solutions.
|
P13-2008-165 (481.843)
Glagolev V.V., Kirillov D.A., Martinska G., Mushinski Ja., Piskunov N.M., Urban J.
Searching and Reconstruction of the Track in the Drift Chambers of the STRELA Setup
Investigation of the drift chambers of the STRELA setup was performed in the beam
of the Nuclotron accelerator complex of the JINR Laboratory of High Energy Physics.
The descriptions of track-finding and reconstruction methods are given. Using of a drift chamber
in the experiment needs correct determination of the distance-to-drift time relation r(t).
This relation is auto-calibrated by an iterative procedure. Knowledge of the correct relation
between the time and space scales allows improving the accuracy of coordinate resolution of
the STRELA drift chambers.
|
P11-2008-169 (689.257)
Amirkhanov I.V., Zemlyanaya E.V., Lakhno V.D., Muzafarov D.Z., Puzynin I.V., Puzynina T.P., Sharipov Z.A.
Numeric Study of the Dynamics of Polaron State
A numerical scheme for solving a system of the nonlinear differential
equations describing the evolution of the polaron in a homogeneous environment has
been investigated. An accuracy of the computational scheme is analyzed. The obtained
results allow us to conclude that if in an initial state the polaron was in a particular
state (basic or excited one), it remains in this state irrespective of the presence or
absence of damping in the system. It is shown that the initial charge distributions given
by some superpositions at presence in the system of damping eventually evolve to a basic
state. No evolution to a basic state is observed at the absence of damping in the system.
|
P11-2008-170 (375.488)
Amirkhanov I.V., Puzynin I.V., Puzynina T.P., Sharipov Z.A.
Mathematical Modelling of Thermal Processes in Materials at Irradiation by Heavy Ions of High Energies
In the work one of the methods of numerical solution of the equations
of mathematical physics - the finite-difference method and its application for the equations
of thermal spike model has been presented. The numerical analysis of convergence
of an explicit finite-difference computational scheme and alternating direction method
is carried out, and also the efficiency and deficiencies of these schemes are explored.
The obtained results of investigation of thermal processes in nickel at irradiation by
uranium ions of the energy 700 MeV with consideration of power losses by phonon oscillations
are represented. The sizes of areas in the target, where temperature exceeds the melting point
of a material of the target and phase changes can take place, are estimated.
A comparative analysis with the model that does not take into account the energy losses
of a heavy ion by phonon oscillations is made.
|
P13-2008-172 (276.245)
Volkov A.D.
Problems of Monitoring the Cryomodule Cold Mass Displacement
The paper deals with the problems of using the wire position monitor (WPM)
for determining the position of superconducting accelerating cavities in the
cryomodule which is the main structure element of modern linear
accelerators. The circuit of matched connection of the WPM into the cold
mass displacement measurement system is proposed. A new appropriately
grounded approach to determination of the relation between the displacement
and the amplitudes of the coordinate electrode signals and the monitor
parameters is developed. This relation takes into account the wire diameter
2R and describes the quantity r with an accuracy order of magnitude better
than the previous one in the range of small displacements r 0,15R. For the first time it is shown that two-strip wire monitors can be
used, which substantially reduces the cost of the cold mass displacement
monitoring system for cryomodules while the measurement accuracy is
preserved.
0,15R. For the first time it is shown that two-strip wire monitors can be
used, which substantially reduces the cost of the cold mass displacement
monitoring system for cryomodules while the measurement accuracy is
preserved.
|
E1-2008-173 (784.378)
G. Bellettini1, J.Budagov2, G.Chlachidze3, V.Glagolev2,
A. Sissakian2, I.Suslov2, M.Trovato1, G.Velev3
(on behalf of the CDF Collaboration)
Top Quark Mass Measurement in the 2.9 fb.1 Tight Lepton
and Isolated Track Sample Using Neutrino ѓУ Weighting Method
We report on a measurement of the top quark mass with t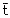 dilepton events
produced in p dilepton events
produced in p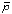 collisions at the Fermilab Tevatron ( collisions at the Fermilab Tevatron (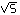 =1.96 TeV) and collected
by the CDF II detector. Events with a charged muon or electron and an isolated
track are searched for tt candidates. A sample of 328 events, corresponding to
an integrated luminosity of 2.9 fb-1, is obtained after all selection cuts. The top
quark mass is reconstructed by minimizing a x2 function in the assumption of
the t =1.96 TeV) and collected
by the CDF II detector. Events with a charged muon or electron and an isolated
track are searched for tt candidates. A sample of 328 events, corresponding to
an integrated luminosity of 2.9 fb-1, is obtained after all selection cuts. The top
quark mass is reconstructed by minimizing a x2 function in the assumption of
the t dilepton hypothesis. The unconstrained kinematics of dilepton events is
taken into account by the scan over the space of possibilities for the azimuthal
angles of neutrinos, and a preferred mass is built for each event. In order to
extract the top quark mass, a likelihood fit of the preferred mass distribution in
data to a weighted sum of signal and background probability density functions
is performed. Using the background constrained fit with 145.0±17.3 events
expected from background we measure mt = 165.5 ± 3,43,3 (stat.) GeV/c2. The
estimate of systematic error is 3.1 GeV/c2. dilepton hypothesis. The unconstrained kinematics of dilepton events is
taken into account by the scan over the space of possibilities for the azimuthal
angles of neutrinos, and a preferred mass is built for each event. In order to
extract the top quark mass, a likelihood fit of the preferred mass distribution in
data to a weighted sum of signal and background probability density functions
is performed. Using the background constrained fit with 145.0±17.3 events
expected from background we measure mt = 165.5 ± 3,43,3 (stat.) GeV/c2. The
estimate of systematic error is 3.1 GeV/c2.
|
E19-2008-174 (448.464)
Chirgadze Yu.N., Ivanov V.V., Polozov R.V., Sivozhelezov V.S., Zheltukhin E.I.
Structural and Electrostatic Regularities in Interactions of Homeodomains with Operator DNA
Interfaces of five DNA-homeodomain complexes, selected by similarity of structures and patterns
of contacting residues were compared. The long-range stage of the recognition process was characterized
by electrostatic potentials about 5  away from molecular surfaces of both protein and DNA. For
proteins, clear positive potential is displayed only at the side contacting DNA, while grooves of
DNA display a strong negative potential. Thus, one functional role of electrostatics is guiding
the protein into the DNA major groove. At the close-range stage, neutralization of the phosphate
charges by positively charged residues is necessary for decreasing the strong electrostatic potential
of DNA, allowing nucleotide bases to participate in formation of protein-DNA atomic contacts in the
interface. The protein's recognizing a-helix was shown to form both invariant and variable
contacts with DNA by means of the certain specific side groups, with water molecules participating
in some of the contacts. The invariant contacts included the highly specific Asn-Ade hydrogen bonds,
nonpolar contacts of hydrophobic amino acids serving as barriers for fixing the protein on DNA,
and interface water molecule cluster providing local mobility necessary for the dissociation of
the protein-DNA compex. One of the water molecules is invariant and located at the center of the
interface. Invariant contacts of the proteins are mostly formed with the TAAT motive of promoter DNA's
forward strand. They distinguish the homeodomain family from other DNA-binding proteins. Variable
contacts are formed with the reverse strand and are responsible for the binding specificity within
the homeodomain family. away from molecular surfaces of both protein and DNA. For
proteins, clear positive potential is displayed only at the side contacting DNA, while grooves of
DNA display a strong negative potential. Thus, one functional role of electrostatics is guiding
the protein into the DNA major groove. At the close-range stage, neutralization of the phosphate
charges by positively charged residues is necessary for decreasing the strong electrostatic potential
of DNA, allowing nucleotide bases to participate in formation of protein-DNA atomic contacts in the
interface. The protein's recognizing a-helix was shown to form both invariant and variable
contacts with DNA by means of the certain specific side groups, with water molecules participating
in some of the contacts. The invariant contacts included the highly specific Asn-Ade hydrogen bonds,
nonpolar contacts of hydrophobic amino acids serving as barriers for fixing the protein on DNA,
and interface water molecule cluster providing local mobility necessary for the dissociation of
the protein-DNA compex. One of the water molecules is invariant and located at the center of the
interface. Invariant contacts of the proteins are mostly formed with the TAAT motive of promoter DNA's
forward strand. They distinguish the homeodomain family from other DNA-binding proteins. Variable
contacts are formed with the reverse strand and are responsible for the binding specificity within
the homeodomain family.
|
P13-2008-178 (334.982)
Li Yong Chan, Pepyolyshev Yu.N., Jang Chang Min
Random Nature in the Dynamics of Slow Power Feedback of the Pulsed Fast Reactor IBR-2
Analysis of the relationship between the parameters of slow power feedback and
power production in the pulsed fast reactor IBR-2 has been accomplished. The investigation result
has shown that unlike the parameters of fast power feedback, the parameters of slow dynamics
are not related to energy production and have considerable noise components. This is caused by
the fact that the slow dynamics of the reactor is generated by the processes in the structural
components around the reactor vessel, in which relatively mild radiation, thermal and mechanical
conditions are observed.
The most possible causes of the random change in the parameters of slow dynamics
from one reactor cycle to another are the irreversibility of displacement of the
stationary reflectors, change in the parameters of the cooling systems of the stationary
reflectors. This randomness in the dynamics of the reactor does not influence the reliability
and safety of the reactor.
|
P13-2008-179 (269.655)
Bulavin M.V., Kulagin E.N., Kulikov S.A., Melikhov V.V., Mukhin K.A.
Determination of Heat Leakage into the Pipeline of Mesitylene Balls for Cryogenic Moderator of IBR-2M Reactor
The modernization reactor of IBR-2 takes place in the
Laboratory of Neutron Physics of the Joint Institute for Nuclear
Research at present. The complex of cryogenic moderators based
on frozen mesitylene balls is included in the modernization plan
of the reactor. The charge of the balls in the chamber of moderators
will be produced by pneumatic transport by cold helium flow with a
temperature of about 40-50 K. The experiments for definition of
heat leakages on the transporting pipe from the quantity of the thermal
protection layers are presented. It is shown that the heat leakage
per unit surface, which can be achieved, is no more than 1 W/m.
|
E1-2008-180 (627.647)
Pozdnyakov V., Vertogradova Yu.
Hadron Azimuthal Correlations to Be Studied at CBM Setup
An opportunity of studying hadron azimuthal correlations with the CBM detector (GSI, Germany) is considered.
The results include the full simulation of the UrQMD events
together with a simplified consideration of the calorimeter near the beam-pipe.
The expectations of the correlations are presented. The centrality determination
is considered via both the charged particles detected in the tracking system and
the energy deposited in the calorimeter. The segmentation of the calorimeter
is discussed from the point of view of the determination accuracy of the reaction plane.
|
E14-2008-181 (425.694)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi niewski R., Altynov V.A. niewski R., Altynov V.A.
State Equations and Molar Volumes of Hydrogen at Super High Pressure
Interpolations of hydrogen experimental molar volumes using logarithm
expansion series and Tait equation in pressure interval from P = 3.0 kbar
to P = 7.0 kbar for four experimental temperatures were carried out.
It was shown that for good approximation of experimental values using
logarithm expansion series only three parameters are necessary. Unfortunately,
such an expansion gives very bad approximation at pressures P< 3.0 kbar. Extrapolations
of molar volumes on high pressures interval up to P=20 kbar using Tait equation and
logarithm expansion series allow one to mention that these different functions give practically
the same values of extrapolating molar volumes at high pressure. One can conclude that mean
distances between hydrogen atoms in high dense hydrogen gas are less than such values in
any saturated hydrides.
|
E14-2008-182 (369.031)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi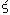 niewski R., Altynov V.A. niewski R., Altynov V.A.
Comparison of Various State Equations for Approximation and Extrapolation
of Experimental Hydrogen Molar Volumes in Wide Temperature and Pressure Intervals
The numerical analysis of practically all existing formulae such as
expansion series, Tait, logarithm, Van der Waals and virial equations for
interpolation of experimental molar volumes versus high pressure was carried
out.
One can conclude that extrapolating dependences of molar volumes versus
pressure and temperature can be valid. It was shown that virial equations
can be used for fit experimental data at relatively low pressures P < 3 kbar
too in distinction of other equations. Direct solving of linear
equation of the third order relatively to volume using extrapolated virial
coefficients allows us to obtain good agreement between existing experimental
data for high pressure and calculated values.
|
E14-2008-183 (976.596)
Didyk A.Yu., Wi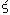 niewski R., Altynov V.A. niewski R., Altynov V.A.
Extrapolation of Hydrogen Molar Volumes by the Virial Equation
on Wide Pressure and Temperature Intervals
A virial equation was used for approximation of experimental molar volumes at
high and low pressures for experimental temperatures. It was shown that the virial
equation can be used for wide pressure and temperature intervals in distinction of the
Tait, logarithm and other equations. The obtained under ftting of experimental data
virial parameters were used for their following extrapolations on wide temperature
intervals. The direct solution of the third order linear virial equations relative to molar
volumes using the Kardano or Neuton methods was employed for extrapolation of
experimental dependences from high pressure to low pressure and from low pressure
to high and superhigh pressures. A quite good agreement between experimental
values of molar volumes versus pressures and extrapolating ones allows one to
conclude that for a defnite temperature interval with high probability and proof it is
possible to make extrapolations on superhigh pressures.
|
P10-2008-185 (260.338)
Maznyy N.G.
Data Transfer Subsystem Between Processes in the Distributed System of Automation
Complexity of systems for automation of experiment (SAE)
is growing alongside with the development of means of computer technology
and programming systems. At the present time requirements to ensure SAE
functioning in distributed environment, availability of hot standby,
dynamic configuring etc. are considered usual.
In any distributed system data transmission facilities play an important role, and
unification of these facilities leads to economy of SAE engineering time and reliability growth.
The present article describes elaborated unified data transmission subsystem, intended
for use in distributed SAE with mixed transmission hardware.
Characteristic feature of this data transmission subsystem consists in the usage of the unified code.
|
7-2008-187
Климан Я.
Исследование динамических эффектов спонтанного деления 252Cf и генерации нейтроноизбыточных ядер в фотоделении
Автореф. дис. ... доктора физ.-мат. наук
(rus)
|
P7-2008-189 (438.445)
Tsyganov Yu.S.
Schmidt Equation: "Flexible" Path Integration
A classic method proposed by K.-H.Schmidt for determining an expected
probability of random correlations assumes some a priori knowledge on the
type of the multiple-link event to single it out of the stochastic stream of
the imitator signals. Here, typical are scenarios with fixed order
or partially free order (taking the signal from recoil nucleus as the first
element of the chain).
The present work considers the case when the elements of order are observed
in an arbitrary location of the multiple-link event. Schmidt's equation is
integrated just for the "flexible" scenario. The problem of organizing
energy intervals for evaluating the probability of random correlations is
also considered. Given are evaluations of the amplitudes of signals from
spontaneous fission in p-i-n diode in the case that the energy scale
is calibrated with the peaks of average light and heavy fission fragments of
the 252Cf source.
Description of the detecting system of the Dubna gas-filled recoil separator
is given in brief, which makes the process of the formation of multiple-link
events in the decay of superheavy elements more understandable to the
reader.
|
P14-2008-192 (339.293)
Rogachev A.V., Kuklin A.I., Chernyj A.Ju., Ozerin A.N., Muzafarov A.M., Tatarinova E.A., Gordelij V.I.
The Structure of Carbosilane Dendrimers of Higher Generations
Using small-angle neutron scattering method, we investigate the structure of
carbosilane dendrimers of the ninth generation with a four-function core and
butyl terminal groups. It is shown that the dendrimers in question are
monodispersive objects having anisometric form. The values of the partial
volume and the mean scattering length density are determined with the
contrast variation method. The studied dendrimers exhibit the same size and
distribution of the scattering length density. It is found that about 20 %
of the interior dendrimer volume is permeable to a solvent. Performing a
Monte Carlo simulation, we reconstruct the spatial distribution of
scattering length density over the dendrimers and reveal changing of the
excluded volume for different contrasts. The spatial structure features of
carbosilane dendrimers of higher generations are discussed.
|
E14-2008-193 (406.569)
Balasoiu M., Kirilov A.S., Kutuzov S.A., Smirnov A.A.,
Kappel W., Cios M., Cios A., Kuklin A.I.
Magnetic System for Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Investigation at
YUMO Instrument of Nanomaterials
SANS measurements using unpolarized neutron beams are able to provide
quantitative information on the magnetic microstructure and the magnitude
and microstructure of the magnetic anisotropy of nanomagnetic materials.
Here we describe a new magnetic system for SANS at YUMO spectrometer.
The system includes 2.5 T electromagnet established on a two-axes
goniometric table, power supply, cooling system, PC-based control equipment.
Main features of magnetic system are: big changeable gap for the samples (up
to 130~mm size), computer controlled horizontal and vertical rotation and
sufficiently large space for the sample holders. The system has been developed
in cooperation with the INCDIE ICPE-CA (Bucharest) and CIPEC SRL
(Bucharest).
First experimental results of SANS in ferrofluids and magnetic elastomers
obtained at YUMO spectrometer equipped with the new magnetic system are
presented.
|
E14-2008-194 (381.885)
Balasoiu M., Craus M.L., Anitas E.M., Bica I., Plestil J., Kuklin A.I.
Microstructure of Dimethylsiloxane Based Magnetic Elastomers
Dimethylsiloxane based elastomers filled with two types of magnetic particles
(nano- and micro-sized) were investigated. It was obtained that doping with Fe3O4
nanoparticles and applying of magnetic field during the polymerization process leads
to a significant change of the local structure of elastomer. After filling the
polymer with Fe3O4 nanoparticles the magnetic elastomer presents a mass
fractal structure. The mass fractal dimension is decreasing in the magnetic elastomer
polymerized in magnetic field. For the elastomer filled with a large amount of Fe
microparticles (75 % particle concentration) a texture effect is detected; for the
samples polymerized in magnetic field the texture effect is higher. Surface fractal
property is obtained for all microparticle concentrations.
|
P13-2008-196 (404.761)
Balandin V.P., Gavrishchuk O.P., Kadykov M.G.,
Kuzmin N.A., Piskunov N.M., Yukaev A.I.
Testing of Hadronic Sampling Calorimeter on 6Li Beam
of Nuclotron
The results of testing the steel-scintillator hadronic calorimeter on
6Li beam of Nuclotron (LHEP) are presented. The measurements were
performed with a matrix assembly of 3 x 3 modules. The transverse size of a
module was 150 x 150 mm, the thickness with respect to the beam is of
4.7 nuclear lengths (40 layers - 20 mm Fe + 5 mm Sc each). The energy
resolution of the calorimeter for deuteron, helium and lithium nuclei with
energy of 2.3 GeV/u are presented. Good agreement of our experimental data
with pion COMPASS data is demonstrated.
|
E2-2008-198 (106.170)
Beshtoev Kh.M.
Computation of the Number of Neutrino Events Which
Can Be Registered in Borexino Detector from the Sun Neutrino Flux
with Energy E = 0.862 MeV = 0.862 MeV
This paper gives an estimation of the number of neutrinos which
can be registered in Borexino detector from the Sun neutrinos
generated in reaction 7Be + e-  7Li + 7Li +  e with
energy E e with
energy E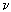 e = 0.862 MeV in the absence of neutrino
oscillations. This number is supposed to be in the range
Ntheor = 86.45 e = 0.862 MeV in the absence of neutrino
oscillations. This number is supposed to be in the range
Ntheor = 86.45  96.52 counts/(day · 100 t) in
dependence on primary neutrino fluxes. Then ratios between the number
of neutrinos Nexper registered in Borexino detector and
counted numbers Ntheor are
Nexper/Ntheor =0.49 96.52 counts/(day · 100 t) in
dependence on primary neutrino fluxes. Then ratios between the number
of neutrinos Nexper registered in Borexino detector and
counted numbers Ntheor are
Nexper/Ntheor =0.49  0.54.
This value is close enough to the same value
obtained in 71Ga-71Ge experiments in the close energy
region. The value Nexper/Ntheor obtained at
the supposition that 0.54.
This value is close enough to the same value
obtained in 71Ga-71Ge experiments in the close energy
region. The value Nexper/Ntheor obtained at
the supposition that  13 13  0 and in the absence of the
resonance effect approximately equals 0 and in the absence of the
resonance effect approximately equals  0.67 and it is
noticeably greater than the above value. Probably it means that
the supposition that 0.67 and it is
noticeably greater than the above value. Probably it means that
the supposition that  13 13  0 is not justified and
there can be a definite deposit of 0 is not justified and
there can be a definite deposit of  neutrinos. neutrinos.
|
P13-2008-199 (388.931)
Kuklin A.I., Utrobin P.K., Ivankov O.I., Sirotin A.P., Gordeliy V.I.
The Hydrostatic High Pressure Setup for the Small Angle Neutron
Spectrometer YuMO
The automated hydrostatic high pressure setup was designed, constructed and
installed at the small angle neutron spectrometer YuMO (Dubna, JINR). It can
produce pressure up to 4000 bar. The scheme, basic elements and structural
features of this device are presented. The procedure of filling pressure chamber with the sample, its positioning in the neutron beam was described. The
neutron scattering curves of lipids and micelles objects were obtained. The
samples were placed in a high pressure chamber connected to the described
setup. The comparison of scattering curves for lipids in the Hellma cells
and in the special pressure cell at p=1 atm was performed. The first
experiments on influence of pressure on lipid membranes and micelles objects
showed high fidelity of the high hydrostatic pressure chamber and its full
adequacy to small angle neutron scattering.
|
E14-2008-200 (390.029)
Balasoiu M., Kuklin A.I., Orelovich O.L.,
Kovalev Yu.S., Arzumanian G.M., Kurkin T.S.,
Stolyar S.V., Iskhakov R.S., Raikher Yu.L.
Structural Investigations of Biogenic Iron Oxide Samples.
Preliminary Results
Some preliminary results on morphology and structure of iron oxide particles
formed inside Klebsiella oxytoca bacteria are presented.
In particular, by means of optical
microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering
the effect of the bacteria age (the duration of growth) on the nanoparticles
properties is studied.
|
E2-2008-201 (160.832)
Gevorkyan S.R. et al.
The Electromagnetic Effects in Ke4 Decay
The final state interaction of pions in Ke4 decay allows one to
obtain the value of the isospin and angular momentum zero   scattering length a00. We take into account the electromagnetic interaction of pions and isospin symmetry breaking effect caused by different
masses of neutral and charged pions, and estimate the impact of these effects
on the procedure of scattering length extraction from Ke4 decays.
scattering length a00. We take into account the electromagnetic interaction of pions and isospin symmetry breaking effect caused by different
masses of neutral and charged pions, and estimate the impact of these effects
on the procedure of scattering length extraction from Ke4 decays.
|
E2-2008-202 (162.041)
Gevorkyan S.R. et al.
The Isospin Symmetry Breaking Effects in Ke4 Decays
The Fermi-Watson theorem is generalized to the case of two
coupled channels with different masses and applied to final state interaction
in Ke4 decays. The impact of the considered effect on the phase of
  scattering is estimated and it is shown that it can be crucial for the scattering lengths
extraction from experimental data on Ke4 decays. scattering is estimated and it is shown that it can be crucial for the scattering lengths
extraction from experimental data on Ke4 decays.
|
P12-2008-204 (204.393)
Filosofov D.V.,
Ion Exchange Behaviour of Ti, Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta as Homologues of Rf and Db in Mixed HF-Acetone Solutions
In order to optimize conditions for isolation and study of chemical
properties of Rf and Db, we investigated sorption of their lighter
homologues Ti, Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta, from HF solutions in water-miscible
organic solvents using the Dowex 50X8 cation exchange (CIX) and AG 1X8 anion
exchange (AIX) resins. We studied dependence of sorption on concentration of
HF (0.1-25 mol/l) and acetone (1-13.6 mol/l). We found that using the AIX resins the distribution
coefficients of Ti, Zr, Hf and Nb increased and those of Ta decreased with
increasing content of acetone in HF solutions. The results indicated that in
concentrated (> 3 mol/l) HF solutions containing acetone, group 4 elements
formed MF73- (M = Ti, Zr, Hf) complexes whose stability decreased
in the order of sorption Zr > Hf > Ti. Under the same conditions, group
5 elements predominantly formed complexes NbOF52- and
TaF72- with stability considerably different, which decreased in
sequence Nb > Ta. We found optimal conditions for separation of the
elements using CIX and AIX chromatography. The advantages of studying
chemical properties of Rf and Db in aqueous HF solutions mixed with organic
solvents are briefly discussed.
|
E11-2008-205 (171.671)
Matej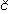 ikov ikov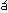 A., T A., T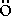 r r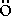 k Cs. k Cs.
Piecewise Smoothing with Two-Part Polynomial Scheme
The present work enhances a recently proposed method for
segmentation and smoothing noisy data that used an autotracking
piecewise reference points based on cubic model and splines. To
overcome the issues with the application of reference points in
approximation tasks a two-part polynomial scheme was elaborated.
This work is a sequel of these results. Its goal is to show that
due to the appropriate localization and assessment of the
reference points, the local approximants of the detected segments
can be not only constructed without the use of splines, but their
number can also be decreased. The method is illustrated with real
data.
|
|
up
|
