Review on role of Aβ peptide in development of Alzheimer’s disease published in Natural Science Review journal
News, 30 April 2025
Scientists from the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research presented a review article devoted to studying molecular mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease in Natural Science Review. This condition is the prevalent type of dementia and one of the most complex neurodegenerative pathologies – nervous system diseases resulting from the gradual degeneration and death of certain neuron groups.
JINR scientists have been studying the properties of cell membranes and cellular interactions since 2019, focusing on the beta-amyloid hypothesis, one of the prevailing explanations for the development of Alzheimer’s. A protein called beta-amyloid peptide (Аβ) can form toxic aggregates (plaques) that accumulate in brain tissues, disrupting the functioning of nerve cells. The mechanisms that trigger this process are still not fully understood.
The review presented in the new JINR journal is devoted to analysing interactions between lipids (fats and fat-like substances found in all living cells) and peptides. In particular, Аβ peptide (residues 25-35) causes the reorganization of lipid membranes (the main components of the cell’s outer protective layer, the cell membrane) in conditions mimicking preclinical Alzheimer’s disease, when destructive processes are already beginning, but no symptoms are present.
Recent studies show that Аβ peptide interacts with the lipid membranes of nerve cells even at relatively low concentrations, which can change membrane structure, disrupting their functions and creating conditions for disease progression.
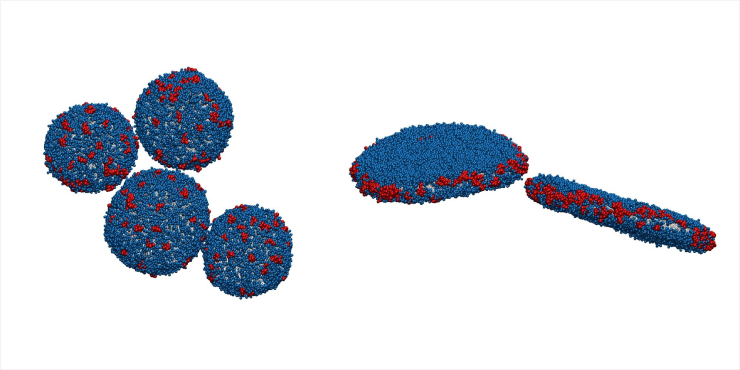 Snapshots of simulations of self-organizing structures of small single-layered vesicles and discs. Grey colour corresponds to lipid chains, lipid head groups are displayed in blue, and Aβ(25–35) molecules are red. Water molecules are not shown for better visualisation
Snapshots of simulations of self-organizing structures of small single-layered vesicles and discs. Grey colour corresponds to lipid chains, lipid head groups are displayed in blue, and Aβ(25–35) molecules are red. Water molecules are not shown for better visualisation
Modern methods of applied nuclear physics are used to analyse these processes. Scattering methods allow studying supramolecular aggregates, spectroscopy makes it possible to obtain information at the molecular level, and computer simulation using molecular dynamics method provides details that are unattainable by experimental approaches.
Recent discoveries confirm that the interaction of Aβ peptide with lipid membranes may be a key factor in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. A deep understanding of these processes brings scientists closer to creating new methods for the prevention and treatment of this complex condition.
The article entitled “Lipid membrane destabilisation induced by amyloid-beta peptide in conditions mimicking preclinical Alzheimer’s disease” was published in the second issue of Natural Science Review in 2025. The authors are JINR employees Sergei Kurakin, Oleksandr Ivankov, Tatiana Murugova (BLTP), Dina Badreeva (MLIT), Ermuhammad Dushanov (LRB), Elena Ermakova, Alexander Kuklin, and Norbert Kucerka (FLNP).